* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Checkpoints
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
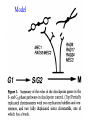
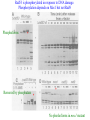
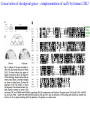
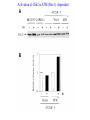
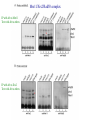
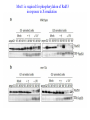
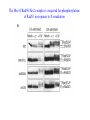
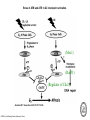
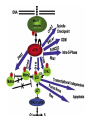
RAD genes rad mutants are hypersensitive to DNA damaging agents X-irradiation UV DNA synthesis inhibitors Possible RAD gene functions Recognize DNA damage and catalyze its repair Recognize DNA damage and activate a checkpoint mechanism that arrests the cell cycle to enable time for repair Irradiation causes cell cycle delay MBC treatment rescues radiation-induced lethality hold in MBC eni wildtype rad9 Diamond: x-ray alone Square: arrest with MBC, release and X-ray Triangle: arrest with MBC, x-ray and hold in MBC for 4 hr rad52 DNA synthesis mutants lose viability in rad9 background Use this phenotype to look for new checkpoint mutants 16,000 mutagenized colonies 500 die rapidly 21 fail to arrest Define 5 genes Checkpoint mutants are sensitive to a variety of DNA damaging agents As expected, checkpoint mutants are indeed defective for cell cycle arrest following irradiation Some G2-phase checkpoint mutants are also defective for an S-phase checkpoint Model Rad53 is phosphorylated in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylation depends on Mec1 but not Rad9 Phosphoforms * Removed by phosphatase * * No phoshoforms in mec1 mutant Conservation of checkpoint genes – complementation of rad53 by human CHK2 human Dros pombe cerev. Human Chk2 is modified in response to irradiation Panels A and B use Ab to identify Chk2 protein Panels C and D show Chk2 mobility shift in response to irradiation Activation of Chk2 is ATM (Mec1) dependent Mre11/Xrs2/Rad50 complex IP with Ab to Mre11 Test with Ab to others * IP with Ab to Xrs2 Test with Ab to others * Mre11 is required for phosphorylation of Rad53 in response to X-irradiation The Mre11/Rad50/Xrs2 complex is required for phosphorylation of Rad53 in response to X-irradiation Roles of ATM and ATR in G2 checkpoint activation. (Mec1) (Rad53) (Regulator of Cdc2) Abraham R T Genes Dev. 2001;15:2177-2196 ©2001 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press