* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Review Sheet ANSWERS
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
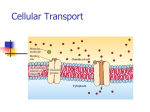
Unit 3 Review Sheet Answers Cell Theory: What are the three parts of the cell theory? - All living things are made of cells - Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things - All cells come from preexisting cells The development of the cell theory is directly related to what invention? Compound light microscope What contribution did the following scientists make to the cell theory: Hooke- Came up with the term ‘cell’ while looking at cork Schleiden- All plants are made of cells Schwann- All animals are made of cells Virchow- All cells come from preexisting cells Cell Parts and Functions: Draw the representative shape of each part and give its function: -Mitochondria- provides the cell with energy; powerplant of the cell -Nucleus- control center of the cell; contains the DNA -Nucleolus- makes ribosomes; dark spot in nucleus -Ribosome- makes proteins -Lysosome- breakdown and clean-up; found in animal cells (not plant) -Endoplasmic Reticulum- transports things around the cell; cell highways -Cytoplasm- water based gel filling the inside of the cell -Centriole- used in cell division, not found in plant cells -Chloroplast- uses sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to make food (glucose); found only in plants; the reason they are green is because of chlorophyll -Vacuole- storage of water, salts and wastes; large in plants -Cell Wall- protection for the cell; not found in animal cells Diversity in cells: What is the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell? Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, eukaryotes do What are 3 differences in animal and plant cells? - Plants have cell walls, animals don’t - Plants have chloroplasts, animals don’t - Plants have large vacuoles, animals have small ones - Animals have lysosomes - Animals have centrioles What is the difference in cilia and flagella? Cilia are many small hairs that move together, flagella are usually one or two whip-like tails. Both are used to move the cell around. Cell Transport: What is the difference between active and passive transport? Passive transport doesn’t need energy and moves molecules from areas of high concentration to low. Active uses energy to move things from low concentration to high. What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? Diffusion is passive transport of solutes, osmosis is passive transport of water across a membrane. What is a hypertonic solution (give an example)? What happens to a cell in a hypertonic solution? A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration in the solution than the cell. Examples: saltwater, syrup. Cells in hypertonic solutions shrivel up/shrink. What is a hypotonic solution (give an example)? What happens to a cell in a hypotonic solution? A hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration in the solution than the cell. Examples: freshwater, distilled water. Cells in hypotonic solutions swell up/pop. Describe the structure of the cell membrane. What is the name of this model? Two layers of phospholipids – bilayer. The phospholipids have proteins mixed in with them and are free to move- Fluid-Mosaic Model Particles too large to pass through protein channels in the cell membrane may enter the cell by: Bulk Transport (exo-, endo-, phago-, pinocytosis) What happens to a cell placed in the following solutions: -hypotonic – water moves in; cell swells, may burst -hypertonic – water moves out; cell shrivels -isotonic – water moves in and out at the same rate; cell stays the same Define the following terms: -facilitated diffusion- diffusion using protein channels, still uses no energy and goes high to low -phagocytosis- bulk transport of solids -pinocytosis- bulk transport of liquids -endocytosis- bulk transport into the cell -exocytosis- bulk transport out of the cell Vocab Review Answers 1. P 2. H 3. EE 4. MM 5. GG 6. E 7. FF 8. NN 9. V 10. VV 11. J 12. HH 13. M 14. U 15. QQ 16. C 17. S 18. N 19. WW 20. O 21. G 22. T 23. BB 24. I 25. II 26. CC 27. W 28. RR 29. LL 30. K 31. PP 32. SS 33. D 34. KK 35. JJ 36. F 37. TT 38. OO 39. Q 40. Y 41. DD 42. Z 43. A 44. AA 45. R 46. L 47. UU 48. X 49. B