* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
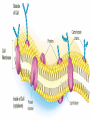
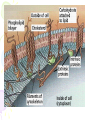
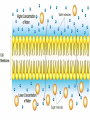
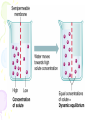
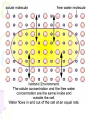
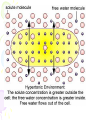
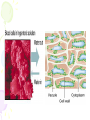
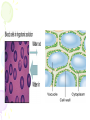
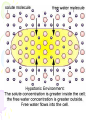
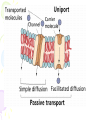
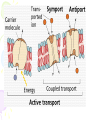
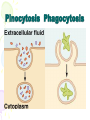
Cell Transport Maintaining Balance • Homeostasis – process of maintaining the cell’s internal environment • Cannot tolerate great change • Boundary between cell and the environment • What provides this? Plasma Membrane • Fluid Mosaic Model • Selective Permeability • Phospholipid bilayer – Hydrophobic; Fatty Acid Tail – Polar Head; Hydrophilic • Cholesterol – Provides stability • Transport Proteins • Carbohydrates • Other Proteins – Cell recognition (immune system) Recall Following Terms • Solution • Diffusion • Concentration gradient • Results in uniform concentration Osmosis • Cells try to reach equilibrium • Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane; 3 results – Isotonic – Hypertonic Tonicity – Hypotonic Isotonic • Solute concentration of solution equal to that of cell • No net water movement Hypertonic • Solute concentration of solution higher than cell • More dissolved particles outside of cell than inside of cell • Hyper = more (think hyperactive); Tonic = dissolved particles • Water moves out of cell into solution • Cell shrinks Hypotonic • Solute concentration of solution lower than cell • Less dissolved particles outside of cell • Hypo = less, under (think hypodermic, hypothermia); Tonic = dissolved particles • Water moves into cell from solution • Cell expands (and may burst) Active vs. Passive • Active vs. Passive Transport • Passive requires no energy from the cell • Active requires cells to use energy, usually ATP Passive Transport • Have to move with the concentration gradient • Diffusion • Osmosis • Facilitated Diffusion- involves use of transport proteins but still follow rule of diffusion Active Transport • Movement of materials against concentration gradient • Transport proteins • Endocytosis – cell takes in material • Exocytosis – expulsion or secretion of materials from cell Pinocytosis Phagocytosis