* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL MEMBRANES CHAPTER 6 FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gap junction wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
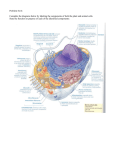
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
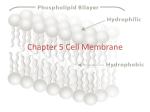
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
CELL MEMBRANES CHAPTER 6 FLUID MOSAIC MODEL REMEMBER THE PHOSPHOLIPIDS? VARIATIONS IN LIPID COMPOSITION Cholesterol content Fatty acids saturation Fatty acids length Affects fluidity PLASMA MEMBRANE PROTEINS Peripheral Integral Proteins are anchored or freely movable Proteins and lipids in the membrane are independent and only interact noncovalently. Or covalently attached and are referred to as anchored membrane proteins. Some move freely This shows the fluidity of cell membranes EXTERNAL CARBOHYDRATES Cell adhesion and cell recognition Glycoproteins and glycolipids Binding occurs with glycoproteins Homotypic Heterotypic CELL JUNCTIONS Tight junctions Desmosomes Gap junctions Integrin attached to Actin TIGHT JUNCTIONS DESMOSOMES GAP JUNCTIONS TRANSPORT ACROSS PLASMA MEMBRANES ACTIVE PASSIVE DIFFUSION OSMOSIS: Diffusion of Water Water will diffuse (net movement) from a hypotonic solution across a membrane to a hypertonic solution. Animal cells may burst when placed in a hypotonic solution. Plant cells with rigid cell walls build up internal pressure that keeps more water from entering—turgor pressure. FACILITATED DIFFUSION Channel proteins Carrier proteins Ion channels (gated, LIGAND OR VOLTAGE, and non-gated) FACILITATED DIFUSSION CARRIER SATURATION GATED CHANNELS MEMBRANE POTENTIAL Unequal distribution ions inside and out of the membrane Na+ outside K+ inside POTASSIUM CHANNEL ACTIVE TRANSPORT PROTEINS •Uniporters Symporters Antiporters PRIMARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT: Sodium-Potassium Pump SECONDARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT BULK SUBSTANCES TRANSPORT PHAGOCYTOSIS PINOCYTOSIS RECEPTOR-MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS Relationship between endocytosis and the “bad” cholesterol Mammalian cells take in cholesterol by receptor-mediated endocytosis. In the liver, cholesterol is packaged into low-density lipoprotein, or LDL, and secreted to the bloodstream. Cells that need cholesterol have receptors for the LDLs in clathrin-coated pits. EXOCYTOSIS OTHER MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS EXCITABLE ENERGY TRANSFORMATION ENZYMATIC REACTIONS PROCESSING INFORMATION