* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
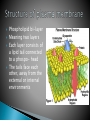
First 10 minutes of class Cell Race Review graphic organizer Notes Cell Test-Tuesday 10/2 Smallest unit of all living things Composed of organelles Each organelle performs specific jobs so the cell can do it’s job Cell membrane Nucleus nucleolus Chromatin Nuclear envelope Microvilli Cytoplasm Mitochondria Golgi body Endoplasmic Reticulum Ribosome Centrioles Describe three organelles discussed yesterday Three lines Discuss cell Continue notes Cell diagram and plasma membrane diagram color and label The barrier surrounding each cell Separates the cells contents from the surrounding environment Is selectively permeable This is the cells way of maintaining boundaries Phospholipid bi-layer Meaning two layers Each layer consists of a lipid tail connected to a phospo- head The tails face each other, away from the external or internal environments Hydrophobic ◦ The lipid tails are water insoluble ◦ They are “water fearing” ◦ They are non-polar Hydrophilic ◦ The protein heads of each Phospholipid is water soluble ◦ They are “water loving” ◦ They are polar and interact well with other polar substances 1. Proteins ◦ a. Peripheral proteins act as binding sites or receptors ◦ b. Integral proteins- proteins that span the membrane act as transport protein ◦ c. Glycoprotein- act as markers, which allow your cells to be recognized as “self” cells 2. cholesterol ◦ Help to stabilize the plasma membrane Channel Proteins ◦ Passive movement of material through pores Carrier proteins ◦ Molecule will bind to the carrier protein causing it to open, allowing passage into the cell Use passive transport ◦ Do NOT require energy ◦ 1. diffusion- molecules move across membrane through pores along a concentration gradient (high to low) ◦ 2. filtration-movement of water and other solutes from high to low concentration Based on a difference in water pressure between external and internal environment Pushes out solutes Occurs in the kidneys Facilitated diffusion◦ concentration gradient still needed ◦ Protein carrier is used because molecules are too large to enter pores ◦ Still passive transport, just needs help ◦ No energy because it is using a gradient Solute Pump (example Na/K exchange pump) ◦ Moves molecules or ions too large to enter on own AGAINST a concentration gradient ◦ REQUIRES ENERGY (active transport) Several junctions are present in order for the cells to continue doing their jobs, while communicating with adjacent cells all the while staying anchored to each other! Membrane junctions: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Tight junctions Desmosomes Gap junctions Microvilli