* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transcription Translation Notes
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
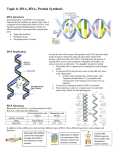
What do we know about DNA? Where is DNA located in the cell? Nucleus What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is a polymer. What is DNA made of? Nucleotides = monomers Function: Stores genetic information = CODE Nucleotide: Hydrogen bonds • Deoxyribose sugar • Phosphate group • Nitrogenous base (A, T, C or G) What do we know about RNA ? What does RNA stand for? Ribonucleic acid What is the name of RNA sugar? Ribose RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine. How many strands does RNA have? One mRNA, rRNA, tRNA The three main types of RNA mRNA carries coded instructions for protein synthesis from nucleus to ribosomes rRNA – ribosome (site of protein synthesis) tRNA – carries specific amino acids to ribosomes during protein assembly What do we know about proteins ? What are proteins made of? Amino acids? What are some examples of proteins? Enzymes, antibodies, hemoglobin, hormones, muscles. What do we know about the genetic code (for a protein) There are four DNA bases: Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine The DNA bases complimentary to each other: A-T & C-G Three nitrogenous bases code for one amino acid (triplet = codon, or a 3-base code) Gene is a section of DNA that codes for a specific protein (sequence of amino acids). Each codon is made up of 3 letters and there are 4 possible letters: How many codons are possible? 4 x 4 x 4 = 43 = 64 possible combinations of codons - Only 20 amino acids are found in proteins Possibilities: - 44 codons (64 – 20) do not code for any amino acid (wasteful) More than 1 codon can code for the same amino acid Universal Genetic Code Learning Check What does the sequence of nitrogenous bases code for? Sequence of amino acids in protein (polypeptide). What is genetic code based on? Codons (triplet bases) What is a gene? A segment of DNA - a code for making a protein. Code Breaker Decode the message hidden in the words Clue: CAPITAL Life Overcomes Nothing Greater Than Itself Minus Everything. Now Only Seems Extremely Easy. Jumping Under Something Terrible, Another Quirkily Useless Idiot Crafted Knives. Verify it Stayed In There To Hurt Openly Unique Goat Herders. The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION Nucleus TRANSLATION Ribosome (cytoplasm) Transcription DNA mRNA gene is copied into mRNA A section of DNA (_____) 1. An enzyme unwinds and unzips DNA (breaks it’s ___________ hydrogen bonds) on the section to be transcribed. Transcription DNA mRNA 2. An enzyme, RNA polymerase, READs the DNA by adding new RNA nucleotides (A; U; C; G) to the _______________ complimentary DNA bases on the DNA template strand. Ex. DNA triplet: TTC GGC ATT AUG CCG UAA mRNA: Transcription DNA mRNA 3. Hydrogen bonds holding mRNA strand to DNA are broken. retwists double helix 4. DNA __________ into its ______________. Transcription DNA mRNA 5. mRNA splicing – before it leaves the nucleus: Introns - noncoding regions (“junk”) Exons – coding regions (will be expressed) Transcription DNA mRNA 6. Transcription is complete. 7. Mature mRNA leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore and travels to the __________ ribosome in the cytoplasm Learning Check Where in the cell does transcription take place? Nucleus What is the purpose of transcription? Make a copy of the DNA message (instructions) for synthesizing a protein. What is the product of transcription? mRNA Why does DNA need a messenger? DNA never leaves the nucleus (too big to exit) TRANSLATION mRNA Protein Process of READING the ________________and mRNA Codons translating them into the language of ______________ AMINO ACIDS (protein). TRANSLATION mRNA Protein Process of READING the ________________and mRNA Codons translating them into the language of ______________ AMINO ACIDS (protein). TRANSLATION mRNA Protein 1. mRNA brings genetic sequence (instructions) to ribosome the ____________ (rRNA) in the cytoplasm to make a _____________. protein AMINO ACIDS TRANSLATION mRNA Protein 2. The rRNA (ribosome) decodes the copy of the DNA code carried by the mRNA in 3 letter chunks called a codon: |**AUG| CCG|UAA| Translation begins with a ***AUG - START codon (Methionine) TRANSLATION 3. Each codon (3 bases) on mRNA corresponds to a specific Amino Acid (AA). There are 20 different AA. TRANSLATION 4. Transfer RNA (tRNA) picks up a floating AA in the cytoplasm and brings it to the ribosome. 5. Here tRNA anticodon meets the mRNA codon to align according to the rules A-U; C-G. 6. Once aligned, tRNA drops its AA off and leaves the ribosome. Another tRNA brings the next AA. TRANSLATION 7. Peptide bonds form between amino acids Protein Sequence = Order of the amino acids TRANSLATION Translation termination 8. Process repeats. Translation continues until it hits a STOP codon (Ex. UAA) and the polypeptide (protein) is released. STOP codons: UAA, UAG or UGA Learning Check Where in the cell does translation take place? Cytoplasm on the ribosome What is the purpose of translation? Translate the language of mRNA codons (bases) to the language of amino acids (protein). What is the product of translation? Protein (polypeptide) An overview of protein secretion in eukaryotic cells: Most protein gets transferred from a RIBOSOME on the ROUGH ER to the Golgi apparatus. Ribosome Step 1: Protein (polypeptide) is transported to the ER. Modification of a protein begins here. Step 2: Transport vesicle Step 3: Intra- take proteins to the Golgi apparatus Golgi vesicle transport Step 4: Proteins that will leave the cell are packaged in secretory vesicles. Proteins that remain in the cell are packaged in lysosomes (digestive enzymes) or storage vesicles. Universal Genetic Code