* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 02_-_translation___mutation_intro - Ms.Holli
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Real-time polymerase chain reaction wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
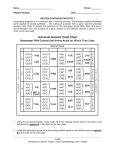
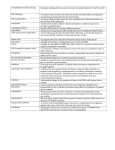
Name: Date: Period: Biology Bell-Ringer: Objective: BWBAT understand the steps in translating mRNA into a chain of amino acids, and 1) Inthe transcription DNAinvolved is used as template to make ____________. describe key molecules inathis process. 2) What is the reason that DNA is not used specifically to make proteins? 3) Create an mRNA molecule using the DNA as a template DNA: TAC GAG CAT mRNA: ______ ______ ______ 4) Where does transcription take place in the cell? THE CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY: Translation: AGC = Serine (Ser) Each codon “codes” for a specific amino acid. For example… CCU = Proline (Pro) Ser Pro GGA = Glycine (Gly) Gly We can use the following chart to determine which amino acid each codon “codes” for: Ala = Alanine Arg = Arginine Asn = Asparagine Asp = Aspartic acid Cys = Cysteine Gln = Glutamine Glu = Glutamic acid Gly = Glycine His = Histidine Ile = Isoleucine Leu = Leucine Lys = Lysine Met = Methionine Phe = Phenylalanine Pro = Proline Ser = Serine Thr = Threonine Trp = Tryptophan Tyr = Tyrosine Val = Valine Codon practice: Identify which amino acid is coded for by each of the following codons: AUG = ___MET__________ GAG = _________________ UUA = _________________ UAU = _________________ CCA = _________________ GCA = _________________ Mutations! What happens when there is a MISTAKE in DNA? READ ME: Even though DNA polymerase proofreads as it replicates a strand of DNA, it occasionally makes a mistake. These accidental changes in the DNA base sequence are called mutations. Mutations can also be caused by environmental factors. There are three types of mutations: 1. insertion2. deletion3. substitutionWe are going to pretend the letters in the following sentence are the bases in a strand of DNA. Imagine that the correct “DNA strand” should read: THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT e Label the three kinds of mutations shown below: THE FAT CAT ATE THE BAT Type of mutation: PFA TCA TAT ETH ERA Type of mutation: ATC ATA TET HER AT Type of mutation: e THE e THF Practice: Original: THE ANT WAS RED 1. Mutation: THB ANT WAS RED 2. Mutation: THE ATW ASR ED 3. Mutation: THE ANT SWA SRE D Looking at the “DNA strands” above, which type of mutation do you think would be the least harmful to an organism? Explain why. Name: Date: Period: Transcription and Translation Practice/Homework Directions: Transcribe the DNA into mRNA. Make sure to use a line or space to separate the codons. Then, use the chart below to translate the mRNA into the proper sequence of amino acids. The first one has been done for you. DNA Strand: AAA GGG GTA CCA TCA TAA CAC CAT mRNA Strand: UUU Amino Acids: Phe CCC CAU GGU AGU AUU GUG GUA Pro His Gly Ser Ile Val Val DNA Strand: TAC TAC GAG CAT CAG CGC TGA ATC mRNA Strand: _____ _____ _____ _____ ____ _____ ____ _____ Amino Acids: _____ _____ _____ _____ ____ _____ ____ _____ DNA Strand: TAC TCG ATG TTT CTT CAT TAT ACT mRNA Strand: _____ _____ _____ _____ ____ _____ ____ _____ Amino Acids: Ala = Alanine Arg = Arginine Asn = Asparagine Asp = Aspartic acid Cys = Cysteine Gln = Glutamine Glu = Glutamic acid Gly = Glycine His = Histidine Ile = Isoleucine Leu = Leucine Lys = Lysine Met = Methionine Phe = Phenylalanine Pro = Proline Ser = Serine Thr = Threonine Trp = Tryptophan Tyr = Tyrosine Val = Valine _____ _____ _____ _____ ____ _____ ____ _____ More Questions: 1. The process by which DNA is used to make mRNA is called ___________________. This happens in the _____________________. 2. The process by which mRNA used to make a protein is called ____________________. This happens in the __________________ of the cell. 3. Proteins are made of long chains of ________________________________. 4. Protein synthesis occurs on what organelle? _________________________. 5. ________ is the type of RNA that brings the amino acids to the ribosome. 6. ________ is the type of RNA that carries the instructions of how to make a protein from DNA. Directions: Transcribe the DNA into RNA, then translate into the 15 amino acids for which it codes. DNA: TAC mRNA: 1 GTT CAA GAT 2 3 4 CGG 5 CTA 6 CGT CAG TCA GTC ATA AAA 7 9 10 11 12 8 amino acids: 1. ____________________ 7. ____________________ 2. ____________________ 8. ____________________ 3. ____________________ 9. ____________________ 4. ____________________ 10. ____________________ 5. ____________________ 11. ____________________ 6. ____________________ 12. ____________________ Mutation Practice: Original: THE CAT HAD FUN 1. Mutation: HEC ATH ADF UN 2. Mutation: BTH ECA THA DFU N 3. Mutation: THE CAB HAD FUN