* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
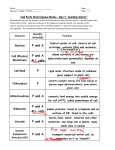
CELLS STRUCTURE & FUNCTION Reading: Chapter 3 Including movement through cell membranes: p. 58-65 (8th edition) p. 59-66 (9th edition) Introduction to Cells The cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Cells come in MANY sizes and shapes. All cells have these 3 parts: 1) Cell membrane 2) Cytoplasm (with organelles) 3) Nucleus CELL STRUCTURES 1. Cell membrane/plasma membrane/plasmalemma a) Structure = phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol = fluid mosaic pattern b) Functions: -gives cell integrity -shape -flexibility -gatekeeper -communication CELL STRUCTURES (con’t) 1. Cell membranes (con’t) c) How molecules move across cell membranes PASSIVE MECHANISMS = NO energy needed 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis ACTIVE MECHANISMS = you NEED energy 3. Active Transport 4. Endocytosis: Pinocytosis & Phagocytosis 5. Exocytosis PASSIVE MECHANISMS 1) Diffusion - movement of molecules -from an area of greater to lesser concentration -NO energy needed (molecules keep moving) PASSIVE MECHANISMS 2) Osmosis -Movement of H2O -From an area of high H2O to low H2O concentration -NO energy needed 2) Osmosis (con’t) Terms to describe osmotic concentration: a) isotonic solution = same salt concentration as the inside of a cell b) hypertonic solution = more salt than a cell c) hypotonic = less salt than a cell What happens to a cell in each of these solutions? ACTIVE MECHANISMS 3) Active Transport -Carriers move molecules from low to high concentration -~40% of energy used by our cells is used to operate these “pumps” -Uses ATP (energy) ACTIVE MECHANISMS 4) Pinocytosis (cell drinking) - This is one type of “endocytosis” - Cell membrane surrounds fluid - The sac pinches off and brings liquid inside ACTIVE MECHANISMS 5) Phagocytosis (cell eating) - This is one type of “endocytosis” Cell membrane surrounds particles Sac pinches off and brings particle(s) inside 6) Exocytosis = the reverse End of mechanisms used to transport molecules across the cell membrane. Back to our list of cell structures. CELL STRUCTURES 2. CYTOPLASM -fluid portion inside cell membrane -organelles are found within this fluid -very structured (microtubules) 3. NUCLEUS -Double membrane separates nucleus from cytoplasm -Contains DNA as chromatin threads -Chromatin clumps up during cell division to form chromosomes (23 pairs) -“Brain” of cell Nucleolus = “little nucleus” - inside nucleus - no membrane - produces ribosomes 4. Ribosomes - “protein factories” - reads genetic code sent from nucleus to build proper protein * * -free in cytoplasm or -attached to RER 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (2 types) a) rough (RER) = “granular ER” - ribosomes attached - ribosomes produce proteins - RER transports proteins b) smooth (SER) = “agranular ER” - no ribosomes attached - transports proteins & lipids - produces steroids - inactivates toxins - stores Ca++ (muscle contraction) CELL STRUCTURES (con’t) 6. Golgi Apparatus - 6 flat sacs - continuous with Endoplasmic Reticulum - separates and packages proteins for export 7. Mitochondria - Oval-shaped - Double membrane - Internal membrane produces energy ATP - Contain DNA (can self-replicate) 8. Lysosomes (lys = split, some = body) - small sacs of enzymes (chemicals) - the enzymes break down molecules - “digestive system” of cell - in apoptosis (programmed cell death) lysosomes are “suicide packets” Enzymes 1ary Lysosome Enzymes + Food/organelle 2ary Lysosome Wastes Residual Body 9) Cilia and Flagella - projections from cell membrane a) Cilia: -many & small -sweeping motion Ex: -respiratory tract -fallopian tubes 9) Cilia and Flagella - projections from cell membrane b) Flagella: -single & large -whip like motion Ex: spermatozoa 10) Centriole - collections of small microtubules - found in pairs (1 pair = centrosome) - separate the chromosomes during cell division Pair = centrosome CELL DIVISION 1) Mitosis - asexual cell division - occurs in most cells - each new cell = identical to original cell - in humans, most cells have 46 chromosomes CELL DIVISION 2) Meiosis - sexual cell division -only occurs in ovaries & testes -each new cell (sperm or egg) only has 23 chromosomes End of Cells