* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Summary Animal Cell Plant Cell
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
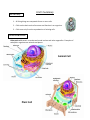
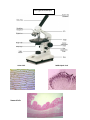
Unit 1 Summary The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. 3. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. Cell Structure & Function Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles. Examples of eukaryotic organisms are animals and plants. Animal Cell Plant Cell Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane bound nucleus. An example is a bacterial cell. Bacterial Cell Organelle Cell Membrane Nucleus Structure Function Helps to maintain a chemical balance between materials inside and outside of the cell. Allows food and oxygen to come into the cell and waste products to move out. Directs all the activities inside the cell. Contains the genetic blue prints for the operations of the cell in the form of (chromatin/chromosomes which contain DNA). Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) Smooth E.R. A gel-like material made out of water, salts, and minerals. Contains the organelles within the cell. A folded membrane that moves materials around in the cell like a conveyor belt. Rough E.R. contains ribosomes. Smooth E.R. does not contain ribosomes. Structures that make proteins in the cells. Stacks of membrane-covered sacs that package and move proteins to the outside of the cell. Rough E.R. Ribosomes *shown attached to the rough E.R. *Ribosomes can also be located suspended in the cytoplasm within the cell. Golgi Bodies Mitochondria Where food molecules are broken down and energy is released. Lysosomes Contains chemicals that digest, or breakdown, wastes and worn-out cell parts. Vacuole Fluid filled temporary storage areas in cells. They may store water, food, and other materials needed by cells while other vacuoles store waste products. Cell Wall A rigid structure outside the cell membrane that supports and protects a plant and a bacterial cell. Chloroplast Organelles in plant cells where light energy is changed into chemical energy in the form of sugar/glucose. Chlorophyll is a green pigment and one of the chemicals in a chloroplast that traps light energy . The Light Microscope Onion Cells Stomach Cells Rabbit Spinal Cord