* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Organelles Worksheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
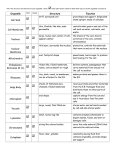
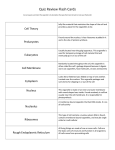
Name: Biology Date: Period: Cell Organelles Worksheet Complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once. Structure/Function 1. Stores material within the cell 2. Controls what moves in and out of the nucleus 3. The sites of protein synthesis 4. Considered the roadways of the cell 5. The region inside the cell except for the nucleus 6. Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell Cell Part Vacuole Nuclear Membrane Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Nucleus 7. Site of photosynthesis in plants Chloroplast 8. Contains enzymes to digest excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria Lysosomes 9. Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum Ribosomes 10. Provides temporary storage of water and food particles Vacuole 11. Firm, protective structure that gives the cell that provides support in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protists Cell Wall 12. Produces a usable form of energy for the cell 13. Packages proteins from rough ER for transport out of the cell Mitochondria Vesicle 14. Organelle that helps breakdown toxins, poisons, and waste Smooth ER 15. Site where rRNA is made Nucleolus 769813568 16. The membrane surrounding the cell, controls what goes in and out of cell. 17. Provides support for the cell, includes cilia & flagella Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton 18. Small membrane-bound sacs used in transport of materials in cells 19. Helps cell maintain shape, helps move cell (if cell moves), helps move things within cell. Vesicles Cytoskeleton 20. Small hair-like structures used for movement or sensing things 21. Composed of a phospholipid bilayer Cilia Cell Membrane 22. Longer whip-like structures used for movement Flagella Put a check in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both. Organelle Plant Cells Cell Wall X Vesicle X Chloroplast X Centrioles Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Mitochondria X X Nucleolus X X Nucleus X X X Plasma membrane X X X Organelle Cytoplasm X X One large vacuole X Cytoskeleton X X Ribosome X Endoplasmic reticulum X X Many small vacuoles Golgi apparatus X X Lysosome X X X In the tables above, circle the three parts that are found in both prokaryotic (bacteria) and eukaryotic (all other living things) cells. *** Study*** 1. The three parts to the cell theory: A. All cells come from cells. B. All living things are made of 1 or more cells. C. The cell is the most basic unit of structure and function in living things. 2. The differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells: Page 2 A. Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus nor do they have membrane bound organelles like a mitochondria, or vacuoles, this is why they are much smaller cells. 3. A. B. C. D. E. F. How proteins are made in the nucleus and moved step by step until the reach the cell/plasma membrane. (we numbered our picture 1-5). Nucleus RER Transport Vesicle Golgi Body Secretory Vesicle Cell Membrane (pushed out) 4. A. B. C. D. The 4 parts that both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells both have. Cell Membrane Ribosomes DNA Cytoplasm 5. The characteristics that make something living. A. Be made of 1 or more Cells B. Response to stimuli C. Reproduction with DNA D. Obtain and Use Energy E. Homeostasis F. Adapt/Variations Page 3