* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neuroscience, 4e
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Binding problem wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
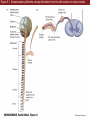
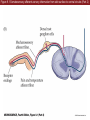
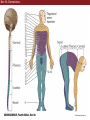
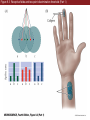
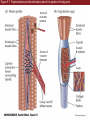
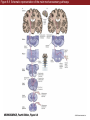
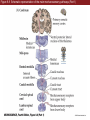
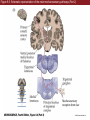
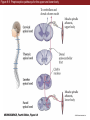
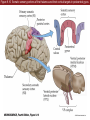
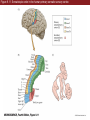
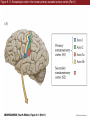
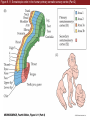
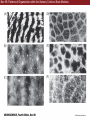
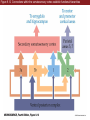
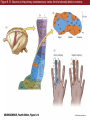
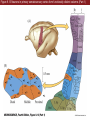
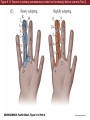
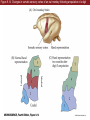
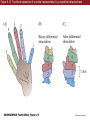
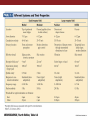
Unit 2 Opener Figure 9.1 Somatosensory afferents convey information from the skin surface to central circuits Figure 9.1 Somatosensory afferents convey information from skin surface to central circuits (Part 1) Figure 9.1 Somatosensory afferents convey information from skin surface to central circuits (Part 2) Figure 9.2 Transduction in a mechanosensory afferent (a Pacinian corpuscle) Box 9A Dermatomes Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold (Part 1) Figure 9.3 Receptive fields and two-point discrimination threshold (Part 2) Figure 9.4 Slowly and rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors respond differently to a stimulus Figure 9.5 The skin harbors a variety of morphologically distinct mechanoreceptors Figure 9.6 Simulated activity patterns in different mechanosensory afferents as Braille is read Figure 9.7 Proprioceptors provide information about the position of body parts Figure 9.8 Schematic representation of the main mechanosensory pathways Figure 9.8 Schematic representation of the main mechanosensory pathways (Part 1) Figure 9.8 Schematic representation of the main mechanosensory pathways (Part 2) Figure 9.9 Proprioceptive pathways for the upper and lower body Figure 9.10 Somatic sensory portions of the thalamus and their cortical targets in postcentral gyrus Figure 9.11 Somatotopic order in the human primary somatic sensory cortex Figure 9.11 Somatotopic order in the human primary somatic sensory cortex (Part 1) Figure 9.11 Somatotopic order in the human primary somatic sensory cortex (Part 2) Box 9B Patterns of Organization within the Sensory Cortices: Brain Modules Figure 9.12 Connections within the somatosensory cortex establish functional hierarchies Figure 9.13 Neurons in the primary somatosensory cortex form functionally distinct columns Figure 9.13 Neurons in primary somatosensory cortex form functionally distinct columns (Part 1) Figure 9.13 Neurons in primary somatosensory cortex form functionally distinct columns (Part 2) Figure 9.14 Changes in somatic sensory cortex of an owl monkey following amputation of a digit Figure 9.15 Functional expansion of a cortical representation by a repetitive behavioral task