* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Artificial neural network wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Recurrent neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
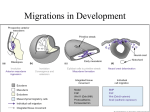
Developmental Biology BIO 442 CHAPTER 13 TERMS TO KNOW The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram describes an experiment, make sure you understand the experiment by being able to describe it in your own words. It is often helpful to look in other chapters of the book to gain a thorough understanding of how the terms are used. Although some terms may not be mentioned in class, as a student of developmental biology you are still responsible for understanding them. Do explore Vade Mecum and the Web sites. NEURAL CREST CELLS Ectoderm Neural crest cells Derivatives of neural crest Fig. 12.1 Peripheral nervous system Adrenal medulla Melanocytes Facial cartilage Dentine of teeth Schwann cells Neuroglial cells Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic nervous system FoxD3 Slug protein RhoB protein HNK-1 protein Types of neural crest cells & their derivatives Cranial neural crest Trunk neural crest Cardiac neural crest Vagal & Sacral neural crest Parasympathetic ganglia Sympathetic ganglia Peristalsis of bowels Congenital megacolon or Hirschprung’s disease Migration pathways of trunk neural crest cells Somite Sclerotome Dermatome Myotome Dorsal root ganglion Ephrin Eph receptor Differentiation of neural crest cell into either sympathetic neuron or chromaffin cell) FGF2 NGF= nerve growth factor Glucocorticoids Pharyngeal arches 4 components of pharyngeal arches Skeletal derivatives of neural crest cells that migrate to pharyngeal arches (table 13.2) Incus Malleus Maxilla Mandible Stapes Hyoid bone Laryngeal cartilages What happens to 5th pharyngeal arch? Hox genes – role in specifying neural crest cell fate Hoxa-3 knockout mouse Hoxa-2 Thyroid gland Parathyroid gland Rhombomere Neural crest cell migration & proliferation Cleft lip Cleft palate Pharyngeal arches 4 & 6 Intramembranous ossification (IO) Mesenchymal cells Osteoblast Osteocyte Osteoid matrix Periosteum Mechansim of IO CBFA1 gene Cbfa1 knockout mice Cleidocranial dysplasia Tooth Development Odontoblast Ameloblasst Endothelium Aortic arch Pulmonary trunk Truncus arteriosus DiGeorge syndrome CATCH 22 Hypocalcemia AXONAL SPECIFICITY Stages of neurogenesis Axon Growth cone Rat hippocampal neuron Synapsin Developmental Biology BIO 442 Motor neuron Retinal neuron Synapse Trophic factor Neuronal plasticity Birth of a motor neuron Sonic hedgehog Targets of motor neurons Zones of motor neurons Column of Terni Medial motor column Lateral motor column Sympathetic ganglia Axial muscles Limb muscles Lim & Islet transcription factors Hindlimb What happens when segment of chick spinal cord is reversed? Steps in axonal connections Pathway selection Target selection Address selection Target cell Substrate Guidance by substrate Physical terrain (anatomical cues) ECM = extracellular matrix Cell surface Haptotaxis Laminin Labeled Pathways Hypothesis Kallman syndrome X-linked trait Anosmia Sterile Olfactory neurons Olfactory epithelium Olfactory bulb GnRH neurons Hypothalamus Guidance by growth cone repulsion Ephrin Sclerotome Semaphorins I & III Collapsin Ti1 neuron Filopodia Cx1 cells Dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons Semaphorin III experiments Transgenic chick fibroblast cells secreting semaphorin III Temperature & pain receptors Mechanoreceptors NT-3 responsive neurons Guidance by diffusible molecules Chemotaxis Netrins 1 & 2 Netrin gradients Floor plate cells Commissural neurons (interneurons) Netrin-1 in situ hybridization Netrin dorsal spinal cord explant experiments Cloning vector Netrin & Trochlear axon experiments Order of events during differentiation of synapse Myotube Agrin Neurotransmitter, Acetylcholine (ACh) Neurotrophic factors = neurotrophins NGF BDNF GDNF NT-3 NT-4/5 Ganglia & neurotrophin experiments Fig. 13.29 Therapeutic uses of Neurotrophins Apoptosis Multiple guidance cues of retinal axons Frog visual system Retina Optic nerve Optic tract Optic tectum N-cadherin Effects of N-cadherin antibodies Mammalian visual system Lateral geniculate nucleus Visual cortex Optic chiasma