* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology 102 A Chapter 7 CFA Standard SB1. Students will analyze
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
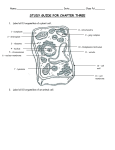
Biology 102 Chapter 7 CFA A Standard SB1. Students will analyze the nature of relationships between structures and functions in living cells. a. Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. 1. Which statement is not a basic principle of the cell theory? a. Most cells come from other cells. b. Cells are the basic unit of structure in an organism c. All living organisms are made up of cells. d. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism 2. Which statement is true about bacterial cells? a. The cells are very large. c. They are eukaryotes. b. The cells have no nucleus. d. They have organelles. 3. The process of the cell membrane using energy to pump sodium out of a cell is called ____. a. diffusion b. osmosis c. active transport d. coupled transport Figure 7-4 4. What would happen to the structure in Figure 7-4 if part D, cholesterol, is completely removed? a. It would become more rigid. c. It would have holes in it. b. It would disintegrate. d. It would collapse in on itself. 5. Where are you least likely to find water in the structure shown in Figure 7-4? a. A b. B c. C d. D 6. Which substance on the cell membrane helps identify chemical signals from outside the cell? a. carbohydrate chain b. cholesterol c. membrane lipids d. transport molecules 7. Which is present in all cells? a. cell membrane b. mitochondria c. cell wall d. nucleus 8. A plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. What will happen to the plant cell? a. It will swell. b. It will shrink. c. It will stay the same. d. It will wilt. 9. Cilia and flagella help to move cells through watery environments. What role do they play on cells that do not move? a. They hold neighboring cells in a fixed position. b. They move substances along the surface of the cell. c. They protect the cell by whipping at harmful cells. d. They transmit waste materials away from the cell. 10. Substances are transported into and out of cells in order to maintain: a. osmosis b. homeostasis c. concentration gradient d. mitosis 11. An electron microscope can magnify an object about 500,000 times. How does this magnification compare with the magnification of a compound light microscope? a. 500 times lower b. 100 times lower c. 100 times higher d. 500 times higher 12.What major improvement came with the development of the scanning electron microscope? a. Magnets were replaced with lighter materials. b. It produced images with better color. c. The magnification was higher. d. The images were three dimensional. 13. What happens in the process of diffusion when dynamic equilibrium is reached? a. the movement of the molecules stops being random b. the molecules are mixed and stop moving c. the rate of change in the solution slows by one half d. there is continuous movement but no change in concentration Use the pictures below to answer questions 14 - 19. Include all choices that are correct!!!! a. b. c. d. e. 14. Which organism(s) are eukaryotic? 15. Which organism(s) would have a cell wall? 16. Which organism(s) are prokaryotic AND have a cell wall? 17. Which organism(s) are unicellular? 18. Which organism would have the largest vacuole? 19. Which organism(s) would have lysosomes and centrioles? 20. Which is present only in eukaryotic cells? a. cell membrane b. chromosomes c. DNA d. nucleus 21. Chloroplasts are the organelles in which photosynthesis occurs. These organelles are found only in plant cells. Which organelle below is found only in animal cells? a. golgi apparatus b. lysosome c. mitochondria d. ribosome 22.Which organelle converts sugars into energy? a. lysosome c. nucleus b. mitochondrion d. ribosome Matching 23. a unicellular organism such as bacteria 24. cells that have a nucleus a. eukaryote 25. cells that have organelles that carry out specific tasks b. prokaryote 26. the first type of cell to evolve 27. A scientist at the polar ice cap was studying an ice sample from hundred of meters below the surface. While examining the ice, the scientist found some cells from many years ago. Using an electron microscope, the scientist identified these cell structures: a cytoskeleton, mitochondrion, nucleus, cell wall, and ribosomes. What kind of organism did the scientist find? a. animal c. plant b. bacteria d. He did not have enough information. Matching 28. where ribosomes are made 29. where proteins are synthesized 30. gets rid of unwanted substances in the cell 31. contains the cell’s DNA 32. stores enzymes 33. acts as a center for packaging cell proteins 34. found outside the cell membrane in some cells a. b. c. d. e. f. g. cell wall Golgi apparatus lysosome nucleolus nucleus ribosome smooth ER 35. A plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution. What will happen to the plant cell? a. It will swell. c. It will stay the same. b. It will shrink. d. It will wilt. 36. Algal cells are placed in an isotonic solution. Additional amounts of solutes are slowly added to the solution. What happens to the cells? a. They will begin to swell. c. They will stay the same. b. They will burst. d. They will shrink. 37. What types of materials are expelled from cells during exocytosis? a. large molecules such as hormones b. positive and negative ions c. small molecules such as carbon dioxide d. water and glycerol 38. Which of the following is an example of passive transport? a. endocytosis c. facilitated diffusion b. exocytosis d. Na+/K+ ATPase pump Each diagram below represents a cell placed in a solution. Match each with the correct solution type. A. 39. Hypertonic solution 40. Hypotonic solution 41. Isotonic solution 42. Which cell might burst? B. C. b. a. c. d. e. 43. What type of cell is represented by the diagram above? a. a prokaryotic, animal cell c. a prokaryotic, plant cell b. a eukaryotic, animal cell d. a eukaryotic, plant cell 44. used to store water 45. controls cells activities 46. site of photosynthesis 47. controls what enters and leaves the cell 48. gives support and protection to cell 49. What is in the cell wall of a plant? a. peptidoglycan b. chitin c. glucose d. cellulose 50. What is the cell wall of a bacterium made of? a. peptidoglycan c. glucose b. chitin d. cellulose