* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory and Cell Structure
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
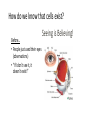
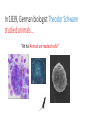
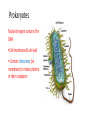
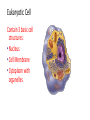
Cell Theory and Cell Structure Central Questions • Who are the scientists who contributed to the cell theory and what did they contribute? • What are the parts of the cell theory? • What are the two largest groupings of cells and what differentiates them? How do we know that cells exist? Before… • People just used their eyes (observations) • “If I don’t see it, it doesn’t exist!” Seeing is Believing! But then, someone invented the microscope! Anton van Leeuwenhoek built one of the first microscopes in the 1600s and saw microscopic organisms. Then they were named… • Robert Hooke cut a piece of oak tree bark called “cork” • Used a microscope • “They look like little rooms!” • “Or like a prison cell!” • He coined the term ‘cell’ Prison Cell vs. Cork Cell So… then many scientists started using the microscope to look at things And their observations made it clear that cells were the basic units of life. In 1838, German botanist Matthias Schleiden studied plants… “Ah ha! Plants are made of cells!” In 1839, German biologist Theodor Schwann studied animals… “Ah ha! Animals are made of cells!” In 1855, Dr. Rudolf Virchow tried to be Frankenstein… but he failed. “We can’t create our own new cells!” “We can only get new cells from already existing cells in our body!” Collaboration is when scientists work together The Cell Theory • All living things are made of one or more cells. • Cells are the basic units in living things. • New cells are produced from existing cells. Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell Number of Cells Organisms may be: • Unicellular – composed of one cell • Multicellular - composed of many cells Cells May be Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic • Prokaryotes include bacteria & lack a nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles • Eukaryotes include most other cells & have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals) Prokaryotes Nucleoid region contains the DNA •Cell membrane & cell wall • Contain ribosomes (no membrane) to make proteins in their cytoplasm Eukaryotic Cell Contain 3 basic cell structures: • Nucleus • Cell Membrane • Cytoplasm with organelles Two Main Types of Eukaryotic Cells Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell Structure • There are two parts outside the cell: - Cell Wall: hard outside covering (not in animal cells) - Cell Membrane: cell ‘skin’ that controls transport in and out Cytoplasm • Water based goop filling the cell • Contains organelles and many compounds Central Questions • Who are the scientists who contributed to the cell theory and what did they contribute? • What are the parts of the cell theory? • What are the two largest groupings of cells and what differentiates them?