* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
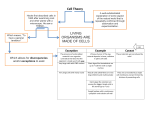
Study Guide Chapter 2, Section 1 – Cell Structure & Function Summary Common Cell Traits All cells have an outer covering called a cell membrane. Cells can be classified as prokaryotic (cells that lack a distinct nucleus) or eukaryotic (cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus). Cell Organization Each cell in your body has a specific function. Most of the cell’s life processes occur in the cytoplasm. From Cell to Organism In a many-celled organism, several systems work together to perform life functions. Self Check 1. Explain why the nucleus is important in the life of a cell. 2. Describe how cell membranes are selectively permeable. Self Check (cont.) 3. Compare and contract the processes of osmosis and diffusion. Why are fresh fruits and vegetables sprinkled with water at produce markets? 4. Discuss how cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are related. 5. Think Critically: How is the cell of a one-celled organism different from the cells in many-celled organisms?