* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Cells- the smallest unit of any living organism
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
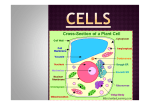
Active Reading: Name _________________________________ Introduction to Cells- the smallest unit of any living organism The first cells to appear on Earth more than 2.5 billion years ago were prokaryotic cells. A prokaryote is an organism made of a single prokaryotic cell. Bacteria are prokaryotes. They are very simple cells that do not have a nucleus. This means that their DNA is not enclosed in a membrane inside the cell. Instead, prokaryotes have a single loop DNA that floats in the cell’s cytoplasm. Like all cells, prokaryotes have a cell membrane to help regulate what can enter and leave the cell. All prokaryotes also have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. The cell wall helps to provide additional support and protection for the cell. Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells. They have double stranded DNA that is found in the nucleus of the cell. The nucleus is an organelle found in all eukaryotic cells that helps to regulate the cell’s functions. Organelles are membrane-covered structures that perform specific jobs inside the cell. Single-celled eukaryotes perform all the functions needed to carry out life. Multicellular eukaryotes are organisms made up of many types of cells each with a specific job or function to perform. Every type of multicellular organism that exists today is made up of eukaryotic cells. Cells are the building blocks of life and are the main focus of a very important theory in biology, called cell theory. This is a way of thinking about living things. Three scientists worked on cells at about the same time. Their names were Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolf Virchow. They came up with the three parts of CELL THEORY. Schleiden worked with plant cells. Schwann worked with animal cells. One night, they had dinner and discussed their work. They realized that plant and animals were both made of cells and that the cells had many similar parts and functions. They went to the lab to look at the cells. They wrote down their findings in 1839. They stated that first, all living things are made of cells and second, the cell is the smallest part of a living organism that can function on its own. The one thing they weren’t sure of was where cells came from. Almost 20 years later, Rudolf Virchow solved the puzzle. Cells, he said, come from other cells. This became the third part of Cell Theory. Cells in eukaryotic organisms can be specialized to perform specific jobs. Cells having the same function are organized into tissues. For example, the epithelial tissue is made of flat cells that build together to act as a protective covering for the body. Different tissues may be found together in structures called organs. The heart is an organ that needs many tissues to move blood. Different organs can work together to form a system. For example, the digestive system is composed of many organs including the stomach, liver, and intestines. All of the many systems help to maintain the metabolism in the organism. The metabolism is the sum of all activities that take place in the organism including digestion, respiration, circulation, and excretion.