* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
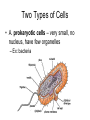
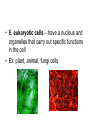
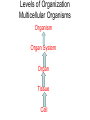
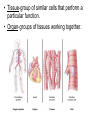
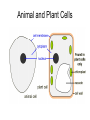
Cells Living Environment Objectives…I can… • Explain the contributions that led to the development of the cell theory. • Describe the levels of organization within organisms. • Describe the structure and function of cell organelles. • Understand the distinguishing characteristics between animal and plant cells. Two Types of Cells • A. prokaryotic cells – very small, no nucleus, have few organelles – Ex: bacteria • B. eukaryotic cells – have a nucleus and organelles that carry out specific functions in the cell • Ex: plant, animal, fungi cells CFU • What are two differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? • Give an example of each type of cell. Cell History • A. 1665 – Robert Hooke observes cork and uses the term “cell” • 1674 – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – makes a single lens microscope • 1838 – Matthias Schleiden – all plants are made of cells • 1839 – Theodor Schwann – all living things are made of cells Cell Theory • A. Cells are the basic unit of life. • B. All organisms are made of one or more cells. • C. All cells come from existing cells. Levels of Organization Multicellular Organisms Organism Organ System Organ Tissue Cell • Tissue-group of similar cells that perform a particular function. • Organ-groups of tissues working together. Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Animal and Plant Cells CFU • Place the following terms in order from simplest to most complex: organ, cell, organism, organ system, tissue