* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELLS-Chapter 2 - St. Thomas the Apostle School
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
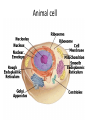
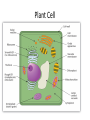
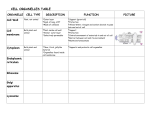
CELLS-Chapter 2 Common cell traits Cell membrane- a cells outer covering And Cytoplasm- gelatinlike substance - CELL TYPES1. Membrane bound structures-Prokaryotic 2. NO membrane-bound structure- Eukaryotic CELL ORGANIZATION Cell wall-a tough rigid outer covering that protects the cell and gives it shape Plant cell- cellulose-long threadlike fibers Cell membrane- Protective layer around all cells a. For cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is inside the cell wall. b. B. a cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste products out of the cell Cytoplasm- gelatinlike substance found in the cell membrane. Many chemical reactions occur within the cytoplasm a. Cytoskeleton- scaffolding like structure in cytoplasm which helps cell keeps its shape. b. In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells have organelles which help with life processes. NUCLEUSContains instructions for everything cell does; includes DNA, powerhouse of the cell. The nucleus directs all cell activities. Energy processing organelles help cells do their work • Green organelles in plant cells contain CHLOROPHYLL to make food • Organelles which release energy from food are called MITOCHONDRIA MANUFACTURING ORGANELLES -RIBOSOMES make protiens for all cell activities -some ribosomes attach to the rough part of the ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM- moves material around in a cell Transporting and Storing Organelles • Golgi bodies- move substances out of a cell to other parts of a cell • Vacuoles- Membrane bound temporary storage spaces • Endoplasmic reticulum- materials are processed and moved around inside the cell; Folded memebranes ENERGY PROCESSING ORGANELLES -In plant cells- chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll trap sunlight to give the plant light energy and chemical energy -Mitochondria-release energy that is needed by the cell from food. Manufacturing organelles Ribosomes- small structures that make their own proteins Recycling Organelles - Lysosomes break down food molecules and cell wastes FROM CELL TO ORGANISM 1. Tissue- group of similar cells working together on one job 2. Different types of tissues working together make up an organ 3. A group of organs working together on a paticular function form an organ system Animal cell Plant Cell Viewing cells Magnifying cellsearly microscopes- lenses made images larger but not always clear Modern microscopes- use lenses to bend light - A simple microscope has one lense while a compond microscope has two sets of lenses. - A Stereomicroscope, which has two eyepieces, creates a three dimensional image. - Powers of the eyepiece multiplied by the objective lenses determine total magnification. Electron Microscope- More powerful than other microscopes. -Uses a magnetic field in a vacuum to bend electronic beams. - Images must be photographed or produced electronically Development of the cell theory 1. The cell theory resulted from many scientists observations and conclusions 2. The basic unit of organization is the cell 3. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 4. New cells come from old cells through cell division VIRUSES • A non –living strand of hereditary material surrounded by a protien coating Virus multiplication- viruses can make copies of themselves only inside a living host cell 1. Active virus- make the host cell produce new viruses , which kill the host cell 2. Latent virus- hide in the host cell without destroying it. - Virus hereditary material becomes part of the host cell’s hereditary material. - latent viruses can become active and the destroy the host cell. VIRUS EFFECTS ON ORGANISMS - Most viruses infect only specific types of cells - Viruses are often carried to the host through the air. - The virus and host cell must fit together exactly to begin a viral infection. - Bacteriophages attach to the bacteria and inject their hereditary material. FIGHTING VIRUSES Vaccines- weakened virus particles which allow the host to fight some diseases Treating a viral disease-antibiotics are NOT effective treatments for viral infections. -infected cells sometimes produce interferons, which are proteins that can protect non-infected cells. - Antiviral drugs often have adverse side effects, limiting their use - - Public health message can prevent or slow disease spread.