* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3-1 cell
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
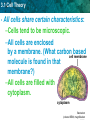
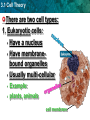
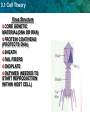
Section 3-1 “Cells” Write everything that is underlined 3.1 Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT: Cells are the Basic unit of life. 3.1 Cell Theory The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. • Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. 3.1 Cell Theory The Cell Theory: 1. All organisms are made of cells • 3.1 Cell Theory 2. All existing cells are produced by other living cells 3.1 Cell Theory 3. The cell is the most basic unit of life 3.1 Cell Theory • All cells share certain characteristics: –Cells tend to be microscopic. –All cells are enclosed by a membrane. (What carbon based cell membrane molecule is found in that membrane?) –All cells are filled with cytoplasm. cytoplasm Bacterium (colored SEM; magnification 3.1 Cell Theory There are two cell types: 1. Eukaryotic cells: • Have a nucleus • Have membranebound organelles • Usually multi-cellular • • Example: plants, animals cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory 2. Prokaryotic cells: • Do not have a nucleus • Do not have membrane-bound organelles • Usually single-celled • Example: bacteria cell membrane 3.1 Cell Theory Viruses MICROSCOPIC PARTICLES THAT INVADE CELLS, OFTEN DESTROYING THEM SMALLEST ORGANISMS IN THE WORLD 3.1 Cell Theory Viruses Are Not Alive VIRUSES ARE NOT CELLS! DO NOT USE ENERGY CANNOT REPRODUCE BY THEMSELVES MUST INJECT GENETIC MATERIAL INTO CELL, CELL THEN FORCED TO MAKE NEW VIRUSES BACTERIOPHAGE • VIRUSES THAT ATTACK BACTERIA 3.1 Cell Theory Virus Structure CORE GENETIC MATERIAL(DNA OR RNA) PROTEIN COAT/HEAD (PROTECTS DNA) SHEATH TAIL FIBERS ENDPLATE ENZYMES (NEEDED TO START REPRODUCTION WITHIN HOST CELL) 3.1 Cell Theory Virus Reproduction VIRUS COMES INTO CONTACT WITH CELL INJECT GENETIC MATERIAL INTO CELL CELL BECOMES VIRUS MAKING MACHINE 3.1 Cell Theory Activity On a blank sheet of paper write down and answer the following questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Summarize the cell theory What do all cells share? Explain the differences between a Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell. Give an example of each. What makes a virus not alive? How do viruses reproduce? 5. On the other side of the paper split the paper in half. Draw, color and label a Prokaryotic Cell and a Virus!