* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SNC 2P Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems Review
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
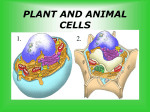
SNC 2P Cells, Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems Review 1. State the three points of the cell theory. 2. Draw a diagram of the cell hierarchy. Explain your diagram. 3. State seven characteristics of living things. 4. State three reasons why cells divide. 5. Explain what a biopsy is and how it can be used to diagnose cancer. 6. State the four components of blood and the function of each. 7. Label the following animal cell. 8. Match the cell organelle to its function. ___ Double layered structure covering entire cell that controls the ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ movement of materials in and out of the cell. An organelle involved in packaging proteins and producing lysosomes. Stores, separates, and serves as cell's transport system. A thick, rigid layer surrounding cell membrane, protects and supports plant cells. Controls and directs all of the cell’s activities. A fluid-filled sac storing food and water for the cell. Sac like structure full of digestive enzymes A jelly-like fluid giving the cell shape and stores wastes. Contains green pigment which helps the plant make its own food through photosynthesis. Stores, separates, and serves as cell's transport system. Covered in ribosomes. Tiny spheres in the cytoplasm or on endoplasmic reticulum. Provides the cell with energy (ATP) through respiration. Long, twisted strands of DNA in the nucleus. Separates nuclear contents from cytoplasm. a) Chromosomes b) c) d) Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell Wall e) f) g) h) i) Mitochondria Lysosome Vacuole Ribosome Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Cytoplasm Chloroplast Golgi Apparatus Nuclear Membrane j) k) l) m) n) 9. Write the six phases of the cell cycle in order. (Be familiar with what each stage looks like) 10. State which phase of the cell cycle (interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase or cytokinesis) each of the following is happening in: _______________________ The chromatids separate. _______________________ The membrane around the nucleus dissolves. _______________________ The cytoplasm divides. _______________________ The chromosomes thicken and become visible. _______________________ The chromosomes replicate. _______________________ A new membrane begins to form around the nucleus at each end of the cell. _______________________ The chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell. _______________________ There are two daughter cells. _______________________ The first phase of mitosis. _______________________ The cell grows. 11. Fill in the missing information in the table about specialized cells. Cell Name Function White Blood Cell Contains hemoglobin that carries oxygen in the blood Muscle Cells Fat Cells Fit tightly together to reduce water loss Sperm Cell Collect calcium to allow growth and repair of the body’s skeleton Photosynthetic cell Conduct electrical impulses to coordinate body activities 12. Fill in the following table based on the four types of tissues. Tissue Description Function epithelial nerve connective 13. What is cancer? Examples 14. Fill in the missing information in the following table Organ Organ system it is part of Function Liver Produces bile to digest fats (chemical digestion) Pancreas Digestive Lungs Respiratory Heart Esophagus Digestive Muscular organ that ‘pumps’ forcing blood throughout the body Trachea Alveoli Arteries Connect mouth to lungs Circulatory Veins Bring blood TO the heart Capillaries Small Intestine Digestive Large Intestine Spinal Cord Brain Salivary glands Absorb water from food/fluid into body Nervous Produce saliva to breakdown food (chemical digestion) and to help move food through the digestive system 15. State the function of each of the organ systems covered (respiratory, circulatory, digestive, nervous, reproductive). 16. State five ways to help prevent diseases. 17. State the organ system of each diagram and label it. Organ System: _________________________ Organ System: _________________________ Organ System: _________________________ Organ System: _________________________ 18. Compare an X-ray, CT Scan, MRI and Ultrasound. 19. What is a vaccine? 20. Explain each the following: a. How the respiratory and circulatory system work together b. How the circulatory system and digestive system work together c. The process of gas exchange 21. Pick a disease studied in class and: a. state the organ system involved b. how it affects the organ system c. the cause d. how to prevent it 22. Explain the difference between the following: a. A tissue stem cell and an embryonic stem cell b. Asexual and sexual reproduction c. Benign and malignant tumour d. Osmosis and diffusion e. Disease and infection f. Pandemic and epidemic g. Chemical and mechanical digestion