* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download nerve net
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
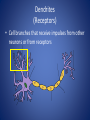
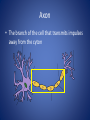
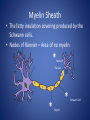
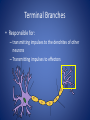
The Nervous System Regulation • The control and coordination of life activities – All organisms use chemicals to regulate life activities – Multicellular animals have NERVE CONTROL – Allow for organisms to maintain HOMEOSTASIS • Stimulus: – Any change in the external or internal environment that initiates a RESPONSE • Response: – A change in BEHAVIOR • Stimuli are detected by RECEPTORS – Sensitive to a particular type of stimulus • Ex. EyesLight, EarsSound • Effectors: – Organs that produce a response to a stimulus • Ex. Muscles and Glands Neuron • Specialized cells which are responsible for transmitting IMPULSES from one part of the body to another • Impulse: – Electrical and chemical changes that travel through neurons – Causes the release of NEUROTRANSMITTERS from terminal branches – **Neuron-Nerve-Ganglia-Brain • Made up of 4 main parts Dendrites (Receptors) • Cell branches that receive impulses from other neurons or from receptors Cyton • The cell body – Contains a nucleus Axon • The branch of the cell that transmits impulses away from the cyton Myelin Sheath • The fatty insulation covering produced by the Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier – Area of no myelin * Node of Ranvier * * Myelin Schwann Cell Terminal Branches • Responsible for: – transmitting impulses to the dendrites of other neurons – Transmitting impulses to effectors Synapses • Junction between adjacent nerve cells • Some nerve cells have junctions with muscles or glands – Chemicals released stimulate contraction of the muscle, or secretion by the gland Neurotransmitters • Chemicals that are secreted by the terminal branch into the synapse between neurons • Carry impulses from one cell to the next – Ex. Acetylcholine and Noradrenaline • Amoeba – No true nervous system • Paramecium – System of FIBRILS that transmit impulses to cilia • Regulates LOCOMOTION and INGESTION • Some species of Protozoans have EYESPOTS • Receive stimuli and generate impulses to produce a response • Hydra – Contain specialized cells similar to neurons, but do not have a central nervous system – Cells connect to form a NERVE NET • Impulses travel in any direction • Earthworm – Has neurons organized into distinct structures and organs which form a TRUE NERVOUS SYSTEM • Brain: – Mass of ganglia located on the dorsal side of the worm, near the head • Ventral Nerve Cord – Main nerve – Connected to the brain and runs along the length of the animal on the ventral side (Belly) • Nerve Branches – Series of smaller nerves that branch to all parts of organism – Impulses are generated by receptors and travel through the nerves to reach muscles and glands • Grasshopper – Similar nervous system to earthworm – Has SENSORY ORGANS • Eyes • Tympanum- Detects sound • Antennae- Sense and Touch A Lateral view B Dorsal view 1 Antenna 2 Brain (cerebral ganglion) 3 Compound eye 4 Tympanum 5 Ganglion 6 Beginning of the Dorsal Nerve Cord 7 Segmental nerves 9 Ventral nerve cord