* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.16 Answers
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
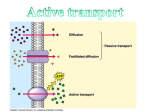
SECTION 1.16 QUESTIONS (Page 71) Understanding Concepts 1. (a) Similarity: Active transport and facilitated diffusion use transmembrane protein carriers to move materials across a selectively permeable membrane. Differences: 1. Active transport uses ATP; facilitated diffusion does not. 2. Facilitated diffusion carries solutes down a concentration gradient; active transport may carry substances against a concentration gradient. (b) sodium ions (Na + ) 2. The two types of endocytosis are phagocytosis and pinocytosis. Phagocytosis occurs when an animal cell engulfs solid particles in the extracellular fluid by surrounding the particles with pseudopods. The pseudopods fuse and enclose the particles and some extracellular fluid in a membrane sac called a food vacuole. In pinocytosis an animal cell takes in a small portion of extracellular fluid by extending pseudopods and forming an extracellular fluid-filled pinocytotic vesicle within the cell’s cytoplasm. 3. Endocytosis is the bulk movement of materials into a cell, from the extracellular environment, by phagocytosis or pinocytosis. Exocytosis is the bulk movement of materials out of a cell, into the extracellular environment, by a process that is essentially the reverse of endocytosis. Both processes are energy consuming. In endocytosis, the cell forms pseudopods around extracellular fluid or particles in the extracellular environment. The pseudopods fuse to form vesicles within the cell’s cytoplasm. In exocytosis, vesicles formed within the cytoplasm, such as those formed by the Golgi apparatus, fuse with the cell membrane, and spill their contents into the extracellular environment. 4. (a) phagocytosis (b) A pseudopod B solid particle C phagocytotic vesicle (c) Lysosomes may fuse with a phagocytotic vesicle and digest its contents. 5. The cell membrane would decrease in size as the membrane pinched off to create phagocytotic or pinocytotic vesicles, without having the membrane being replaced through exocytosis. 6. hormones and enzymes NEL Section 1.16 25 Applying Inquiry Skills 7. (a) Hypothesis: The sugar molecules are transported into the cell membrane by active transport because the concentration of sugar molecules move into the cell against a concentration gradient over time. (b) This observation reinforces the student’s hypothesis because a cell would have to produce large amounts of ATP to power the active transport process that moves sugar molecules into the cell by active transport.