* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
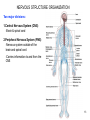
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
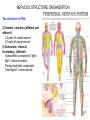
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
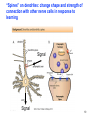
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
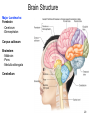
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
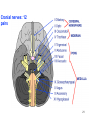
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
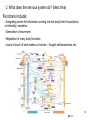
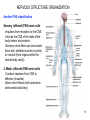
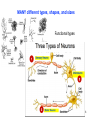
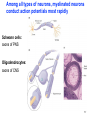
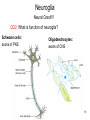
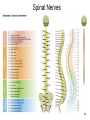
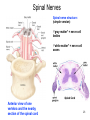
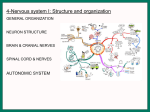
4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization GENERAL ORGANIZATION NEURON STRUCTURE BRAIN & CRANIAL NERVES SPINAL CORD & NERVES AUTONOMIC SYSTEM Announcements Andrew’s Office Hours: Friday 9:00-10:00, Higgins 520 Meghan’s Office Hours: Wednesday 6:30-7:30 (pm!), Higgins atrium Quiz 1: Issued Today by 5:00, due Friday by 5:00 Scaling basics: geometric similarity (large organisms could be (but are not necessarily) just geometrically scaled-up versions of small organisms) Metabolism, as well as structure, is scaled…. Predicting LSD dosage for a large animal…… 0.5-1.0 mg/kg is the minimum to cause a “transient rage” 6.5 mg/kg is lethal. 0.1 - 0.2 mg causes mental disturbance QQ1: Is Tusko especially sensitive? 0.02 mg/kg causes psychotic symptoms 297 mg (= 0.10 mg/kg) was administered to “Tusko”, a male Indian elephant (West et al. 1962). West, L. J., C. M. Pierce and W. D. Thomas. 1962. Lysergic acid diethylamide: its effects on a male Asiatic elephant. Science 138:1100-1103. Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. 10 Q: What is the nervous system? A network of billions of nerve cells linked together in a highly organized fashion to form the rapid control center of the body In the brain, roughly 100 billion (1011) neurons and 100 trillion (1014) synapses (connections between nerve cells) 11 Q: What does the nervous system do? (Next time) Functions include: –Integrating center for information coming into the body from the periphery or internally; sensation –Generation of movement –Regulation of many body functions –Locus of much of what makes us human – thought self-awareness, etc. 12 NERVOUS STRUCTURE ORGANIZATION Two major divisions: 1.Central Nervous System (CNS) -Brain & spinal cord 2.Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) -Nervous system outside of the brain and spinal cord -Carries information to and from the CNS 13 NERVOUS STRUCTURE ORGANIZATION Two divisions to PNS: i) Somatic; voluntary (afferent and efferent) -12 pairs of cranial nerves -31 pairs of spinal nerves ii) Autonomic; visceral; involuntary; (efferent) -Sympathetic component (“fight/ flight”; thoraco-lumbar) -Parasympathetic component (“rest/digest”; cranio-sacral) 14 NERVOUS STRUCTURE ORGANIZATION Another PNS classification Sensory (afferent) PNS nerve cells -impulses from receptors to the CNS -Informs the CNS of the state of the body interior and exterior -Sensory nerve fibers can be somatic (from skin, skeletal muscles or joints) or visceral (from organs within the ventral body cavity) 2. Motor (efferent) PNS nerve cells -Conduct impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles) -Motor nerve fibers (both autonomic and somatic/voluntary) 15 MANY different types, shapes, and sizes Functional types 16 Among all types of neurons, myelinated neurons conduct action potentials most rapidly Schwann cells: axons of PNS Oligodendrocytes: axons of CNS 17 Neuroglia Neural Crest!!!! QQ2: What is function of neuroglia? Schwann cells: axons of PNS Oligodendrocytes: axons of CNS 18 “Spines” on dendrites: change shape and strength of connection with other nerve cells in response to learning Signal Signal 19 Brain Structure Major Landmarks: Forebrain -Cerebrum -Diencephalon Corpus callosum Brainstem -Midbrain -Pons -Medulla oblongata Cerebellum 20 Cranial nerves: 12 pairs 21 Spinal Nerves 22 Spinal Nerves Spinal nerve structure: (simple version) -“gray matter” = nerve cell bodies -“white matter” = nerve cell axons Anterior view of one vertebra and the nearby section of the spinal cord 23 Spinal Nerves QQ2: What integrates the afferent and efferent signals? (code 6681) 24 CNS CNS = brain + spinal cord; all parts of interneurons are in the CNS PNS PNS: (1) afferent neurons (their activity “affects” what will happen next) into the CNS & (2) efferent neurons (“effecting” change: movement, secretion, etc.) projecting out of the CNS. 25 Contrast autonomic and somatic components of the nervous system 26 Contrast autonomic and somatic components of the nervous system Voluntary Command: MOVE! Involuntary Command: Rest/Digest Involuntary Command FIGHT! FLIGHT! Skeletal Muscle Contraction Heart, smooth muscle, glands, etc. Heart, smooth muscle, glands, etc. 27 Schematic diagram of the mammalian autonomic nervous system 28 Another schematic diagram of the mammalian autonomic nervous system 29