* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells, specialised cells and diffusion (Quick Questions) 1. What is
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
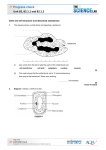
Cells, specialised cells and diffusion (Quick Questions) 1. What is the function of the cell membrane? 2. What is the function of the cell wall? 3. What is the function of the vacuole? 4. What is the function of chloroplasts? 5. What is the function of the mitochondria? 6. What is the function of the ribosomes? 7. What is the function of the cytoplasm? 8. What are plasmids? 9. Name 3 parts that a plant cell has but an animal cell doesn’t. 10. Name a difference between a bacteria cell and an animal cell. 11. Name a difference between a yeast cell and an animal cell. 12. Name 3 ways of sperm cell is adapted to its function. 13. Name 2 ways a root hair cell is adapted to its function. 14. What is diffusion? 15. Describe how particles move in diffusion. 16. What is the difference between two areas of concentration called? 17. When will diffusion take place quickly? Cells, specialised cells and diffusion (Quick Answers) 1. Controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell. 2. It strengthens the cell. 3. It keeps cells rigid and supports the plant. 4. 5. They contain chlorophyll that absorbs light energy to make food by photosynthesis. Structures in the cytoplasm where respiration takes place. 6. Structure where protein synthesis take place (new proteins are made). 7. It is a liquid gel in which most of the chemical reactions take place. 8. These are found in bacterial cells and are small circular bits of DNA. 9. Vacuole, cell wall and chloroplasts. 10. An animal cell has a nucleus whereas bacterial cells have plasmids. 11. A yeast cell has a cell wall but an animal cell doesn’t. 12. It has a long tail to help it swim, the middle part is full of mitochondria so that energy is provided by respiration for the tail to work and the acrosome (head part) stores digestive enzymes for breaking down the outer layers of the egg. 13. The root hairs increase the surface area for water to move into the cell and the cells have a large permanent vacuole that speeds up the movement of water. 14. Diffusion is the spreading out of the particles of a gas or any substance in a solution. 15. Particles move from an area of high concentration to low concentration. 16. Concentration gradient. 17. When there is a big difference in concentration between two areas.