* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
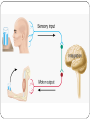
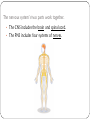
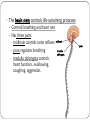
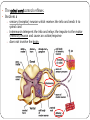
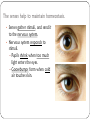
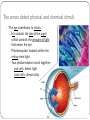
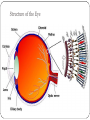
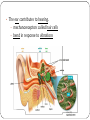
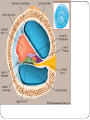
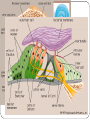
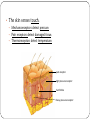
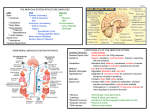
KEY CONCEPT #3 The central nervous system interprets information, and the peripheral nervous system gathers and transmits information. The nervous system’s two parts work together. • The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord. • The PNS includes four systems of nerves. • The CNS and PNS pass signals between one another. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Sensory receptor generates impulse. PNS passes impulse to CNS. CNS interprets impulse. CNS passes impulse to PNS. PNS stimulates a response . The CNS processes information. • The brain processes, interprets signals and generates responses. • Made up of three parts: – cerebrum controls thought, movement, emotion – cerebellum allows for balance – brain stem controls basic life functions Brain stem midbrain pons medulla oblongata • The brain stem controls life-sustaining processes • Controls breathing and heart rate • Has three parts: – midbrain controls some reflexes – pons regulates breathing – medulla oblongata controls heart function, swallowing, coughing, aggression. midbrain pons medulla oblongata • The spinal cord controls reflexes. • Involves a – sensory (receptor) neuron which receives the info and sends it to spinal cord – interneuron interprets the info and relays the impulse to the motor (effector) neuron and causes an action/response – does not involve the brain The PNS links the CNS to muscles and other organs. • The somatic nervous system regulates voluntary functions like muscle movement • The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions like digesting food, breathing • sympathetic nervous system: controls “fight or flight” response Details: Raises heart rate • parasympathetic nervous system: calms the body Details: conserves energy; lowers heart rate KEY CONCEPT #4 The senses detect the internal and external environment stimuli. The senses help to maintain homeostasis. • Senses gather stimuli, and send it to the nervous system. • Nervous system responds to stimuli. – Pupils shrink when too much light enters the eyes. – Goosebumps form when cold air touches skin. Types of Sensory (receptors) Neurons Mechanoreceptors: detects pressure, touch stretch, motion, and vibration Photoreceptor: detects visible light Chemoreceptor: detects chemicals in the air Thermoreceptors: responds to temperature differences Pain receptors: detects pain The senses detect physical and chemical stimuli. • The eye contributes to vision. – Iris controls the size of the pupil which controls the amount of light that enters the eye – Photoreceptors located within the retina sense light. – Two photoreceptors work together: – rod cells: detect light – cone cells: detect color Structure of the Eye • The ear contributes to hearing. – mechanoreceptors called hair cells – bend in response to vibrations Interpreting sound Pinna (auricle) collect the sound Sound waves travel down the auditory canal Sound waves hit the tympanic membrane (eardrum) causing it to vibrate Vibrations are carried along the tiny bones in the ear called the malleus, incus, and stapes. Eventually, the vibrations reach the organ of Corti which bends the hair cells When the hair cells are stimulated, an impulse is sent down the nerve fibers. • Taste and smell use chemoreceptors. – Taste uses tongue, and smell uses nose. – Chemoreceptors detect chemicals dissolved in fluid. • The skin senses touch. • Mechanoreceptors detect pressure. • Pain receptors detect damaged tissue. • Thermoreceptors detect temperature. pain receptor light pressure receptor hair follicle heavy pressure receptor