* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download a positive electrical signal
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
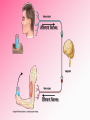
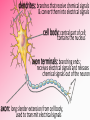
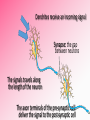
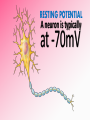
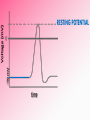
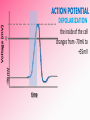
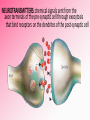
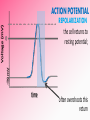
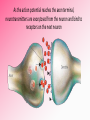
Afferent Nerves Efferent Nerves dendrites: branches that receive chemical signals & convert them into electrical signals cell body: central part of cell; contains the nucleus axon terminals: branching ends; receives electrical signals and releases chemical signals out of the neuron axon: long slender extension from cell body; used to transmit electrical signals Dendrites receive an incoming signal Synapse: the gap between neurons The signals travels along the length of the neuron The axon terminals of the pre-synaptic cell deliver the signal to the post-synaptic cell RESTING POTENTIAL A neuron is typically at -70mV ACTION POTENTIAL a positive electrical signal at +35mV -70 mV Voltage (mV) RESTING POTENTIAL time RESTING POTENTIAL A transport protein forces ions against their concentration gradients 3 sodium (Na+) molecules are pushed outside the cell 2 Potassium (K+) molecules are pushed inside the cell There is a net removal of positive ions (cations) outside the cell; inside of the cell becomes negative ACTION POTENTIAL -70 mV Voltage (mV) DEPOLARIZATION the inside of the cell changes from -70mV to +35mV time NEUROTRANSMITTERS: chemical signals sent from the axon terminals of the pre-synaptic cell through exocytosis that bind receptors on the dendrites of the post-synaptic cell DEPOLARIZATION The binding of neurotransmitters to the receptors of dendrites triggers the opening of a few Na+ channels This causes a slightly positive charge When the charge reaches the threshold (-55mV), many voltagecontrolled Na+ channels open, causing a flood of positive charges All-or-None Principle ACTION POTENTIAL -70 mV Voltage (mV) REPOLARIZATION the cell returns to resting potential; time often overshoots this return REPOLARIZATION As Na+ channels close, K + gates open. K + rushes out of the cell, returning to the cell to a -70mV resting potential As the action potential reaches the axon terminal, neurotransmitters are exocytosed from the neuron and bind to receptors on the next neuron https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SdUUP2pMmQ4 Select one of the following neurotransmitters and be prepared to share its role with the class Acetylcholine Dopamine Norepinephrine & Epinephrine Serotonin Histamine