* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Notes – Life Science Section 2.1 – Cell Structure 2 Main Typ
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
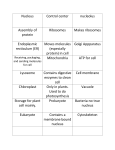
Chapter 2 Notes – Life Science Section 2.1 – Cell Structure 2 Main Types of Cells – Prokaryotic – Cells without membrane bound structures -‐ NO TRUE NUCLEUS -‐ Ex. Bacteria Eukaryotic – Cells with membrane bound structures -‐ Has a TRUE NUCLEUS -‐ Ex. Plant or Animal Cells Cell Wall – Outer covering of a cell -‐ Protects cell and gives the cell shape ** Plants, algae, fungi and most bacteria have cell walls ** Cell Walls are mostly made of cellulose, but they also have pectin and lignin. Cell Membrane – Outer covering of the cell -‐ Regulates what comes in and out of the cell Cytoplasm – Gel-‐like material that organelles move in Cytoskeleton – made up of thin, hollow tubes that help the cell maintain or change shape Organelles The largest organelle is the NUCLEUS. Nucleus – Directs all cell activities -‐ Contains DNA Nucleolus – Found inside the nucleus – “little nucleus” Chloroplasts – Makes food for the cell -‐ Contain chlorophyll ** Chlorophyll captures energy to make sugar (glucose). Mitochondria – Release Energy Ribosomes – Make proteins -‐ Some are attached to the ER and some float freely Endoplasmic Reticulum – moves materials around in the cell -‐ Smooth ER -‐ no ribosomes attached -‐ Rough ER – ribosomes attached Golgi Bodies – sort and package substances Vacuoles – Store food, water or waste Lysosomes – Breakdown food, waste and worn out cell parts Levels of Organizations 1) Cell 2) Tissue 3) Organ 4) Organ System 5) Organism