* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Intro to Cells
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
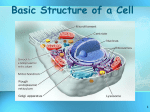
Chapter 7 Pages 168-193 ……what does it mean to be living? Mrs. Brown Rocks! •Be based on a universal genetic code •Grow and develop •Be able to reproduce *Sexually *Asexually •Use materials and energy- metabolism •Be able to respond to their environment *Stimulus Response •Maintain stable internal environment- homeostasis •Change over time, as a group- evolution •Made of units called cells Cells in organisms are specialized to perform different tasks. Muscle Blood NOT Skin Brain Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism Atom Element Molecule Compound Cell •Basic units of life; perform special jobs Tissue •Similar cells function together Organ •Different tissues function together Organ System •Different organs function together Organism Cell Theory Matthias Schleiden Theodore Schwann all plants are made of cells all animals are made of cells Cell Theory Rudolf Virchow all cells came from pre-existing cells Animal Cell Plant Cell •All living things are composed of cells •Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things •New cells are produced from existing cells Cell Types PROKARYOTE EUKARYOTE • No nucleus • No membrane-bound organelles • Small ribosomes • Most cells are 1 -10 μm in size • Evolved 3.5 billion years ago • Found only in Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Kingdoms • • • • Has nucleus Many organelles Larger ribosomes Cells can be between 2 1,000 μm in size • Evolved 1.5 billion years ago • Includes Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia Kingdoms Cell Type: Prokaryotes • Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria, are the simplest cellular organisms. They have genetic material but no nucleus. Typical bacteria cell Cell Types: Eukaryotes • Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and numerous membrane -enclosed organelles (e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus) not found in prokaryotes. What Are the Parts of Cells • Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have some things in common. nuclear cell membrane ribosomes cytoplasm material • All cells have – – – – cell membrane cytoplasm ribosomes genetic material