* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
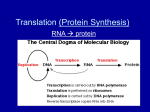
LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea: 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable information. a. The sequence of RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA molecule, determines RNA function. o o o o mRNA carries information from the DNA to the ribosome. tRNA molecules bind specific amino acids and allow information in the mRNA to be translated to a linear peptide sequence. rRNA molecules are functional building blocks of ribosomes. The role of RNAi includes regulation of gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription b. Genetic information flows from a sequence of nucleotides in a gene to a sequence of amino acids in a protein. 1. The enzyme RNA-polymerase reads the DNA molecule in the 3’ to 5’ direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. Examples include o Addition of a poly-A tail o Addition of a GTP cap o Excision of introns 3. Translation of the mRNA occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosome. o The mRNA interacts with the rRNA of the ribosome to initiate translation at the (start) codon. o The sequence of nucleotides on the mRNA is read in triplets called codons. o Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart. Many amino acids have more than one codon. Memorization of the genetic code is beyond the scope of the course and the AP Exam. o tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. o The amino acid is transferred to the growing peptide chain. o The process continues along the mRNA until a “stop” codon is reached. o The process terminates by release of the newly synthesized peptide/protein. o KEY TERMS: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, transcription, uracil, polymerase, introns, exons, condon, anticodon, ribosome, translation, polypeptide, protein, initiation, elongation, termination, mutation, insertion, deletion, transposon, McClintock