* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6 Active Transport 0809
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
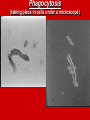
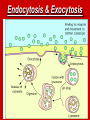
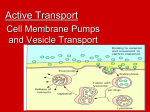
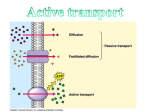
Active Transport Cell Membrane Pumps and Vesicle Transport Active Transport Active transport - movement of materials AGAINST the concentration gradient from low concentration to high concentration Requires the cell to use energy (ATP) 2 kinds: 1. membrane pumps 2. vesicle transports 1. Cell Membrane Pumps Involve carrier proteins called cell membrane pumps to move materials against the concentration (UP concentration gradient) Similar to the steps of facilitated transport. Results in electrical impulses across nerve cells Ex. Sodium-Potassium Pump 2. Vesicle Transport Some substances (ex. Food) are too BIG to pass through membrane OR large quantities need to pass through the cell These situations use vesicle transport Two kinds 1.Endocytosis 2.Exocytosis Endocytosis Cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules & large particles (including other cells) External materials are enclosed by part of the cell, forming a pouch The pouch pinches off cell membrane & becomes a membrane bound organelle called a vesicle Vesicles can fuse with lysosomes to digests contents. Two kinds of Endocytosis: 1. Phagocytosis – movement of large particles or whole cells. *Possible feeding method, or a method of defense to destroy bacteria/viruses 2. Pinocytosis – transport of solutes or liquids Phagocytosis Pinocytosis (cartoon animation) (cartoon animation) Phagocytosis (taking place in cells under a microscope) Endocytosis Exocytosis (Reverse of endocytosis) Vesicles in cytoplasm fuse with cell membrane and RELEASE their contents into the external environment OUTSIDE the cell Used to release large molecules such as proteins packaged by the golgi apparatus Used in nervous & endocrine system to control activities in other cells. Exocytosis Endocytosis & Exocytosis Endocytosis • http://www.maxanim.com/physiology/Endo cytosis%20and%20Exocytosis/Endocytosi s%20and%20Exocytosis.htm