* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Membrane and Transport
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
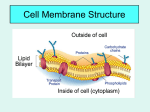
DO NOW (WRITE Q AND A IN SOURCEBOOK) 1. 2. 3. What are some things that pass through a window screen? What are some things that cannot pass through a window screen? Why is it important to keep these things from moving through the screen? The cell is surrounded by a membrane which regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Why is it important to regulate what moves into and out of a cell? MEMBRANE AND TRANSPORT Video Introduction: The Cell Membrane King https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6fhbbFd4icY&l ist=UUb2GCoLSBXjmI_Qj1vk-44g THE CELL MEMBRANE selectively permeable: Let in stuff they need, kick out stuff they don’t need. To get into the cell, materials must pass through the cell membrane. Two reasons this is important: 1. How cells acquire what they need and get rid of what they don’t 2. How cells communicate with one another PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER Cell membranes are made out of phospholipids. There are hydrophilic (water loving) and hydrophobic (water hating) parts. TYPES OF TRANSPORT Two categories of transport: active and passive Passive transport doesn’t require any energy. Diffusion: transport of stuff (oxygen). Particles want to spread out. Osmosis: transport of water. Osmosis and Diffusion are examples of PASSIVE transport. They don’t require any energy. ACTIVE TRANSPORT Channel proteins act like hallways. Active transport moves things in the opposite direction of the concentration gradient. SOLUTIONS: 3 TYPES Solution: something dissolved in water (salt, the solute) Hypertonic Hypotonic Isotonic The kidneys regulate the concentration of blood plasma. HYPERTONIC the solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell water moves out HYPOTONIC the solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell water moves in ISOTONIC concentration of solute same inside cell as outside (balanced) water moves in and out When things transport to attempt to become isotonic it’s called: moving across the concentration gradient Blood DO NOW: COPY THE PICTURE. LABEL HYPERTONIC, HYPOTONIC, OR ISOTONIC. DRAW AN ARROW SHOWING THE DIRECTION THE WATER WILL MOVE. DO NOW: IN SOURCEBOOKS The cell membrane is made up of a _____ bilayer. A) Carbohydrate B) Lipid C) Protein D) None of the Above True or False: All cells have a cell membrane. The lipids in the bilayer have tails that are _____ meaning that they repel (or do not like) water. True or False: Some molecules can pass through the bilayer without help. WRITING TO WIN: FOCUSED FREE WRITE 6-7 sentences 5-6 key terms Prompt: I am _______, the lipid bilayer. Key terms: Cell membrane structure surround hydrophilic lipids movement semipermiable properties bilayer Double hydrophobic proteins DO NOW: Mrs. Stoops has a saltwater fish (Nemo) that she put into a freshwater fish tank. What will happen to the fish and why? Draw a sketch to illustrate your answer. Hint: Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic Swell Shrink Balanced VOCABULARY BINGO Homeostasis Phospholipid Fluid mosaic model Cell membrane Selective permeability Receptors Diffusion Concentration gradient Osmosis Hypertonic Hypotonic Passive transport Facilitated diffusion Isotonic Active transport Phagocytosis Endocytosis Exocytosis Hydrophilic Hydrophobic Kidneys Protein channel Pinocytosis Turgid