* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8-Animal and Plant Cells lesson 8 in pdf
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
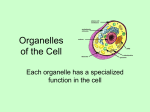
Animal and Plant Cells Lesson 8 Let’s Review! ∗ All living things are made of what? ∗ A-Cells ! ∗ How many organ systems is the human body made of? ∗ A-Eleven. Now, name them. ! ∗ What organ system is responsible for breaking down food and disposing of waste? ∗ A-Digestive Cells ∗ All living things are made of cells. ∗ Plant and animal cells contain many structures which do different jobs inside the cells. ∗ Plant and animal have many structures in common. However, plant cells contain some structures that animal cells do not contain. ! ∗ In this lesson, you will learn about the various parts that make up plant and animal cells. ∗ You will have to label and identify the functions of the organelles. Examples of Cells Amoeba Proteus Plant Stem Bacteria Red Blood Cell Nerve Cell Two Types of Cells 1) Prokaryotic 2) Eukaryotic The Two Types of Cells ∗ All living things fit into one of two categories based on their cell structures. ! ∗ #1-Prokaryote ∗ A prokaryote is made up of one or more cells that do not contain a nucleus. Prokaryotes are generally tiny, single-celled organisms. Prokaryotic ! ∗ Do not have structures surrounded by membranes ∗ Few internal structures ∗ They are usually single-celled organisms (unicellular), such as bacteria ∗ They are the smallest cells in the world. ∗ The DNA is long and circular shaped like a rubber band. ∗ We will not dwell on these. http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html Type #2-Eukaryotes ∗ Eukaryotes do contain a nucleus. ∗ Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotes. ∗ They are ten times larger than prokaryotic cells. ∗ The DNA is linear and is in the nucleus. ∗ Most eukaryotes are made up of many cells that work together. ∗ You have these cells in your body. Eukaryotic ! ∗ Contain organelles surrounded by membranes ∗ Most living organisms are eukaryotic. Plant http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html Animal Cell Structures ∗ Again, plant and animal cells have many of the same structures, or contents. ∗ Plant cells have parts that animal cells do not have. ∗ The cell parts that carry out a specific job are called organelles. ∗ Let’s look at both plant and animal cells and their parts. “Typical” Animal Cell http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/NSC/images/cell.gif “Typical” Plant Cell http://waynesword.palomar.edu/images/plant3.gif Organelles Surrounding the Cell Cell Membrane ∗ The outer membrane ∗ It is a thin covering. ∗ Flexible ! Job: * Controls movement of materials into and out of the cell * SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE ! --> Double layer (heads & tails) http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cell Wall ∗ Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria ∗ Stiff, more rigid than cell membrane ∗ Not found in animal cells ∗ Made of a strong fiber called cellulose. The cells of plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria are enclosed in a cell wall. ∗ Cell walls are tough, rigid outer coverings that protect cells and give them shape. ∗ Job: ∗ Supports & protects plant cell ∗ Gives the plant cell its rigid, boxlike shape ∗ Allows material in & out Organelles Inside the Cell Nucleus Job: ∗ A large structure inside the cell that contains the cell’s genetic material. ∗ Directs/manages cell activities ∗ The “brain” of the cell-contains the DNA Nuclear Membrane ∗ Surrounds nucleus ∗ Has nuclear pores openings that allow material to enter and leave nucleus http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chromosomes ∗ Inside the nucleus ∗ Made of DNA ∗ Contain instructions for traits and characteristics ∗ Involved in mitosis and meiosis ! ★ Humans have 23 pair = 46 total http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cytoplasm Cytoplasm ∗ Clear gel-like fluid that fills the organelles ∗ All cells contain cytoplasm. ∗ A variety of structures are located in the cytoplasm. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) ∗ A system of folded membranes that serve as passageways in a cell. ∗ Moves materials around in cell through the ER to other areas. ∗ Series of tubular passageways ∗ The ER also makes proteins, fats, and other materials ∗ Breaks down drugs and other substances ∗ Smooth type: lacks ribosomes ∗ Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Ribosomes ∗ Each cell contains thousands ∗ They are the smallest organelles ∗ Tiny grain-like structures ∗ “Protein factories” - site of protein manufacturing ∗ They hook together amino acids to make proteins. http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Mitochondria ∗ For materials to move around the cell, energy must be made. ∗ The mitochondria produces energy through chemical reactions – breaking down fats and carbohydrates and releases energy. ∗ The “powerhouse” of the cell; the energy produced is used to power all the organelles. This process is called cellular respiration. ∗ The energy of the cell is called ATP. The Golgi Complex ∗ When proteins are made in the ER, they then go to the Golgi apparatus. ∗ It is known as the protein “packaging plant”-it attaches proteins from the ribosomes to sugars, starches, and fats. ∗ It modifies and sends proteins to other parts of the cell or out of the cell to go somewhere else Lysosome ∗ All cells produce wastes. ∗ The lysosome is the digestive organelle for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates ∗ The lysosomes contain substances called enzymes, which break down wastes. ∗ Breaks down wastes and unwanted or “broken” cell material or large materials ∗ The “garbage disposal” of the cell ∗ The lysosome’s membrane prevents the digestive chemicals inside from leaking into the cytoplasm and destroying the cell. ∗ When a cell dies, the lysosome’s membrane disintegrates, releasing digestive chemicals that allow the quick breakdown of the cell’s contents. http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Lysosomes Vacuoles ∗ Used for storage ∗ They store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates that the cells need. ∗ Helps plant cells maintain shape ∗ Animal cells have several small vacuoles. ∗ They are MUCH larger in plants cells. http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Chloroplast ∗ Chloroplasts are organelles only in plant cells that capture light energy from the sun. ∗ Contains chlorophyll a green substance that absorbs light and gives plants their green color ∗ They make food for plants; photosynthesis takes place here. http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Cells! ∗ Cells are the building blocks of life. ∗ The cell was discovered by Hooke. ∗ In 1665, Robert Hooke cut a thin slice of cork and looked at it under his microscope. ∗ To Hooke, the cork seemed to be made up of empty little boxes, which he named cells. ∗ The word cell in Latin means “little rooms”. ∗ The cell theory states that ∗ 1) Cells are the smallest units of life 2) All living organisms are made up of cells 3) All cells come from preexisting cells ∗ All cells must constantly take in nutrients, store, produce, and breakdown substances, and take in and use energy. If the parts of a cell could talk… ∗ Who would say… I have a way with amino acids! ! I’m the garbage man! ! You can find everything in me! ! I’m the “brain” of the cell. ! I have all the “power” you’ll need. ! I’m found all “around” a plant cell. 1. RIBOSOME 2. LYSOSOME 3. CYTOPLASM 4. NUCLEUS 5. MITOCHONDRIA 6. CELL WALL I have a way with amino acids! ! I’m the garbage man! ! You can find everything in me! ! I’m the “brain” of the cell. ! I have all the “power” you’ll need. ! I’m found all “around” a plant cell. What about these? ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ I’m needed for food. ! I’m the outside of an animal cell. ! You name it – I can store it! ! I make ribosomes. ! I work with the ER. ! I’m full of genetic information. 1. CHLOROPLAST 2. CELL MEMBRANE 3. VACUOLE 4. NUCLEOLUS 5. GOLGI BODY 6. Genes/Chromosomes I’m needed for food. ! I’m the outside of an animal cell. ! You name it – I can store it! ! I make ribosomes. ! I work with the ER. ! I’m full of genetic information. A Lab-What if our school were a cell? ∗ Our school is like a cell in several ways. ∗ We have a waste system, a powerhouse, a central command, etc. ∗ Your job in this lab is to label the parts of our school as if it were a cell. ∗ Using construction paper-cut the sheets in half. ∗ You will write the parts of a cell and label the parts of our school that correspond to those parts. ∗ The cell part and the reason why you chose that part go on the front. The part of our school goes on the back. ∗ Do not enter any classrooms or the office. You also may not leave the building. ∗ Here are the parts-cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts, vacuole, cytoplasm, ribosomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes. Cell Review #1 ∗ MULTIPLE CHOICE ∗ Rough endoplasmic reticulum has _____attached to it. ∗ A. Ribosomes ∗ B. Golgi bodies ∗ C. Chloroplasts ∗ D. Lysosomes ∗A #2 ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ A group of cells that work together to do one job is called… A. Organ system B. One celled organism C. Tissue D. Organ C ! ∗ https://www.youtube.com/watch? v=rABKB5aS2Zg&safe=active