* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geuvadis Analysis Meeting
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Alternative splicing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA-binding protein wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
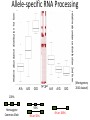
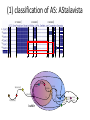
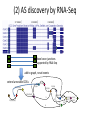
Geuvadis Analysis Meeting 16/02/2012 Micha Sammeth CNAG – Barcelona Quantification of Splice-Forms and Variants - Quantified 615 datasets based on the Gencode v7 annotation - Sensitivity is a function of sequencing depth - For every transcript, normalized RPKM values and number of deconvoluted reads Correlation coeff. 0.87 (Pearson and Spearman) - Discussion at the end if/what to do before uploading LoF Definitions [MacArthur et al. 2012] LOF = loss of function of a complete transcript LoF types SNP that introduces (directly) stop codon Indels that disrupt/shift reading frame X SNP that disrupts splice site Larger deletions that remove 1st exon or >50% of transcript LoF scope “partial” LoF affects just some protein-coding transcripts in a locus X X “full” LoF affects all protein-coding transcripts annotated Large deletion 116 Frameshift indel X Splice 267 337 565 Stop across populations X Large deletion 24 12 Splice in a single individual 23 38 Frameshift indel Stop LoF Estimates [MacArthur et al. 2012] Compare RNA-Seq evidence to LoF predictions main difference Geuvadis <> 1000 Genomes: RNA-Seq vs. DNA-Seq Frameshift indel Large deletion } X X X X directly from mappings / coverage by mappings X predicted disruption of splice site indirectly called from mappings Confirmation LoF SNPs in Geuvadis Stop - Take phase1 samples where polymorphisms have been found by exome sequencing - Additionally call SNPs by RNA-Seq (exzessive mappings) ~5000 differences, i.e. on average >2 out of 1000 calls differ Example: (not Geuvadis) Sufficient coverage in DNA >2 million genotype calls possible in both Experiments Sufficient coverage in RNA ~1000 cases where RNA is homozygous and DNA not could be explainable by allele-specific expression ~4000 cases where DNA is homozygous and RNA not (!!!) remove FPs from computational or experimental artifacts (PCR artifacts?) Allele-specific RNA Processing relative abundance distribution 1st form relative abundance distribution 2nd form A/A A/G G/G 1st 2nd A/A A/G G/G 100% Homozygote Common Allele 50% 0% or 50% 0% or 100% [Montgomery 2010 dataset] LoF and Alternative Splicing (AS) “28.7% LoF events in a single individual affect only a subset of the known transcripts from the affected gene, Emphasizing the need to consider alternative splicing” [MacArthur et al. 2012] (1) classification of AS influences in LoF based on a certain annotation 5’ frame 2 3’ frame 0 2 1 2 0 (2) extension of an annotation by RNA-Seq evidence X X ? activation of latent splice sites (1) classification of AS: AStalavista 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 ^ [ 1,2,3,6 - - 1,2,3,6 ^ 1,3,5,6 1,2,3,6 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 ^ ^ 6 3,5,6 5 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 bubble 2 1 4 - 3,5,7 - 1,4 ^ 1,2,3, 4,5,7 - 1,2,3, 4,5,7 ] (2) AS discovery by RNA-Seq Novel exon junctions supported by RNA-Seq add to graph, novel events 7 extend annotated CDSs 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 ^ [ 1,2,3,6 - - 1,2,3,6 ^ 1,3,5,6 1,2,3,6 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 ^ - ^ 6 3,5,6 5 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 2 1 4 - 3,5,7 - 1,4 ^ 1,2,3, 4,5,7 - 1,2,3, 4,5,7 ] My Points • Quantifications: do you want a normalization before uploading or is this in the responsibility of the analyzing group? • Quantifications: • Timeline for studies—main paper Oct-end of the year. • Separate publications possible if there is sufficient material for a separate story? • What would be the constraints for a separate publication on Geuvadis data? Acknowledgements Thasso Griebel (PhD): Error Models, Pipelining Paolo Ribeca(PhD), Santiago Marco: GEM mapper + conversion Emanuele Raineri (PhD): SNP calling