* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Transport - PickensAPBiology
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
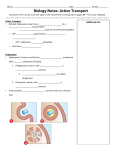
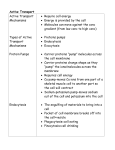
Active Transport Movement of molecules against the concentration gradient “uphill” Allows cell to maintain internal concentrations of small molecules Specific proteins embedded in membranes Energy provided by ATP Transfer of phosphate to induce conformational change in the protein Types of active transport: Uniport=movement of a single molecule Symport=movement of two molecules in the same direction Antiport=movement of two molecules in opposite directions An example of active transport: Membrane potential Uneven balance of charged ions across the membrane -50 to -200 mv Cytoplasm is negative compared to outside of cell Favors passive transport of cations into cell and anions out of cell Electrochemical gradient Chemical gradient Electrical gradient (follows same principle as chemical gradient) Concentration of Na+ in a cell at rest is lower than outside the cell Gated channel opens Sodium “fall” down concentration gradient (toward outside of cell) Electrogenic pump Na-K pump Active pump contributes to membrane potential 3 Na+ out=2 K+ in Transfer of one (=) charge for every cycle Proton pump Transports protons (H+) out of cell Harnesses energy to do work The Na+/K+ pump in action: Co-transport Flow of one solute molecule through a pump indirectly drives movement of other solutes Couples downhill diffusion with uphill tranport Examples Proton gradient (established by proton pump) transports amino acids, sugars (sucrose) into cell How sucrose is loaded into cells in the veins of a plant Active Vs. Passive Transport: A Review Transport of large molecules Proteins and polysaccharides Exocytosis: removal of particles Transport vesicles produced by golgi Fuse with plasma membrane Excretory cells Vesicle-mediated transport: Exocytosis Exocytosis in action: Endocytosis Endocytosis: engulfing of particles Plasma membrane forms a pocket Pinches inward forming a vesicle Phagocytosis Wrapping pseudopodia around particle Forms a membrane enclosed vesicle Contents digested by lysosome Pinocytosis “gulping” droplets of extracellular fluid Unspecific transport Receptor mediated endocytosis Very specific Extracellular substances bind to ligands of cell surface Enables cell to acquire bulk quantities of specific substances that may be in low concentration in ECM Cholesterol buildup in blood vessels Cholesterol travels in blood stream in low density lipoproteins LDL’s bind to receptors on membranes and enter cell by endocytosis Defective LDL receptors prevents uptake of cholesterol by cell Results in accumulation in blood stream Contributes to atherosclerosis Vesicle - mediated transport: Endocytosis Pinocytosis Vesicle - mediated transport: Endocytosis Phagocytosis Receptor-mediated endocytosis Check yourself Explain the difference between passive and active transport and give specific examples of each Explain the difference between gated channels, electrogenic pumps and cotransport. Give specific examples of each Explain the difference between exocytosis, pinocytosis, phagocytosis and receptor mediated endocytosis. Useful links http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/tran sport/atpase.swf http://student.ccbcmd.edu/~gkaiser/biotutorials/photo syn/atpasep.html http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/an imations/active1.swf http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olc/dl/120068/bio04.swf