* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download structure and function of the cell
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
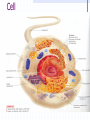
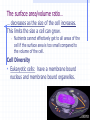
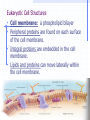
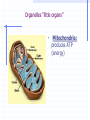
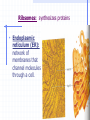
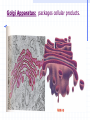
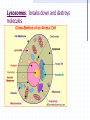
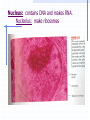
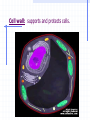
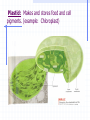
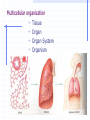
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE CELL CHAPTER 4 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION- CHAPTER 4 VOCABULARY (33 words) 1. 4. 7. 10. 13. 16. 19. 22. 25. 28. 31. Cell Cytoplasm Prokaryote Tissue Phospholipid bilayer Nucleolus Endoplasmic reticulum Cytoskeleton Cilium Cell wall chlorophyll 2. Cell theory 5. cytosol 8. eukaryote 11. organ 14. chromosome 17. ribosome 20. Golgi apparatus 23. microtubule 26. flagellum 29. plastid 32. chloroplast 3. plasma membrane 6. nucleus 9. organelle 12. organ system 15. nuclear envelope 18. mitochondrion 21. lysosomes 24. microfilament 27. centriole 30. central vacuole 33. thylakoids Cell The Cell Theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. • Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism. • Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells. • The surface area/volume ratio… … decreases as the size of the cell increases. This limits the size a cell can grow. • Nutrients cannot effectively get to all areas of the cell if the surface area is too small compared to the volume of the cell. Cell Diversity • Eukaryotic cells: have a membrane bound nucleus and membrane bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells: do not have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles Eukaryotic Cell Structures • Cell membrane: a phospholipid bilayer • Peripheral proteins are found on each surface of the cell membrane. • Integral proteins are embedded in the cell membrane. • Lipids and proteins can move laterally within the cell membrane. Organelles “little organs” • Mitochondria: produces ATP (energy) Ribsomes: synthesizes proteins • Endoplasmic reticulum (ER): a network of membranes that channel molecules through a cell. Golgi Apparatus: packages cellular products. Lysosomes: breaks down and destroys molecules Microfilaments and microtubules: comprises the cellular framework and helps the cell to divide when it reproduces. Cilia (hairs) and flagella (tails): cause cellular movement. Nucleus: contains DNA and makes RNA. Nucleolus: make ribosomes Cell wall: supports and protects cells. Vacuoles: stores enzymes and waste products. Plastid: Makes and stores food and cell pigments. (example: Chloroplast) Multicellular organization • • • • Tissue Organ Organ System Organism Evolution of multicellular organization 1. Prokaryotic cells are found first in the fossil records 2. Eukaryotic cells appear later in the fossil record. 3. Colonial organisms 4. Multicellular organisms