* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to the Cell
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
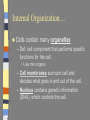
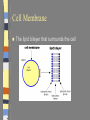
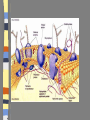
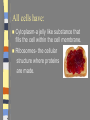
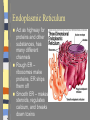
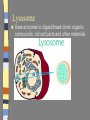
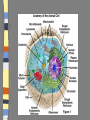
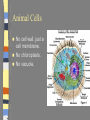
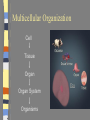
Introduction to the Cell Chapter 7.1 Introduction to the Cell Cell- smallest unit of matter that can carry on all of the processes of life Hooke and Leeuwenhoek used microscopes to see first images of cells in the 1600-1700’s. The Cell Theory… a. All living things are composed of cells b. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in an organism (smallest living unit). c. Cells come only from the reproduction of existing cells (cells come from cells). Cells Size… Limited in size because of surface to area ratio – If a cell gets too big the nutrients and wastes do not have enough surface area to come into / out of the cell Shape… A cells shape is usually associated with its job. Internal Organization… Cells contain many organelles – Def: cell component that performs specific functions for the cell • Like mini organs – Cell membranes surround cell and decides what goes in and out of the cell. – Nucleus contains genetic information (DNA), which controls the cell. Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Eukaryotic – Cell that has membrane bound organelles – More complex – Plant and animal cells -YOU are a eukaryote! Prokaryotic – Has membrane around entire cell – No organelles – No nucleus – bacteria Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic Bill Nye: Discovery of Cells Organelles Inside the Eukaryotic Cell 7.2 Cell Membrane The lipid bilayer that surrounds the cell Cell Membrane cont. Controls what enters/leaves the cell Selectively permeable – allows some substances to enter while not allowing others to enter Sometimes have proteins integrated into the layer, some are on either side of the bilayer All cells have: Cytoplasm-a jelly like substance that fills the cell within the cell membrane. Ribosomes- the cellular structure where proteins are made. Nucleus Contains DNA, hereditary info. Surrounded by the nuclear membrane Also has a nucleolus where ribosomes are made. The cell’s “brain.” Mitochondria Site of chemical reactions that produce ATP (energy). Have folded center to allow for more surface area for production of ATP Have their own DNA Many of them in the cell Ribosomes Numerous; some are free floating others are attached to Endoplasmic Reticulum Play a large role in the production of proteins Endoplasmic Reticulum Act as highway for proteins and other substances, has many different channels Rough ER – ribosomes make proteins, ER ships them off Smooth ER – makes steroids, regulates calcium, and breaks down toxins Lysosome Uses enzymes to digest/break down organic compounds, old cell parts and other materials Golgi Apparatus Processes and packages cells proteins Cytoskeleton ~ Provides support and allows movement like a human’s skeleton. Cilia and Flagella Cilia Found on outside of the cell Aid in movement Hair-like structures Cilia are short and come in large numbers Flagella Found on out side of the cell Aid in movement Hair-like structures Flagella usually come in 1-3. Plant vs. Animal Cells Both plants and animals have more complex eukaryotic cells. However there are some differences in there structure. Plant Cells… Have cell wall for structural supportlike plant bones Has large vacuoles for storage of water and toxins Have Chloroplasts that convert light into chemical energy Animal Cells No cell wall, just a cell membrane. No chloroplasts. No vacuole. Levels of Organization From Cells to Organisms 7.3 Multicellular Organization Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organisms Multicellular Organization Cell=The smallest unit of life. Tissue= A group of similar cells that are working together. Examples: Muscle tissue or bone tissue. Organ= Similar tissues organized into a structure with a specific function. Examples: Heart, bones, liver. Multicellular Organization Organ system- Various organs working together to carry out a major body function. Examples: digestive system, urinary system, reproductive system. Organism-Any living thing that can carry out life processes independently.