* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Under what conditions do cells gain or lose water - kis
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
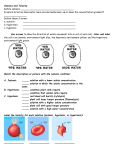
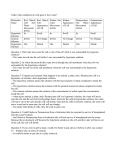
The Nature of Science: Under what conditions do cells gain or lose water? Use the website given on the catalyst or the following: http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html Molecules name Red blood cell: Net water movement In / Out Red blood cell: Appearance of cell Elodea: Net water movement In / Out Elodea: Appearance of cell Paramecium: Net water movement In / Out Paramecium: Appearance of cell Hypotonic solution Isotonic solution Hypertonic solution 1. Did water move into the cell or out of the cell while it was surrounded by hypotonic solution? (think about each cell) 2. In which direction did the water move through cell membrane when the cell was surrounded by the hypertonic solution? 3. Compare and contrast what happens to an animal cell, a plant cell, and a Paramecium cell in a hypotonic, and isotonic and a hypertonic solution. 4. Could Elodea or Paramecium from a freshwater lake be expected to survive if transplanted into the ocean? Explain. 5. If you were to grill a steak, would it be better to put salt on it before of after you cooked it? Explain why, in terms of osmosis. 6. Why does salad become soggy and wilted when the dressing has been on it for a while? Explain why, in terms of osmosis. 7. An effective way to kill weeds is to pour salt water on the ground around the plants. Explain why the weeds die, using the principles discovered in this Virtual Lab.