* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cytoskeleton
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
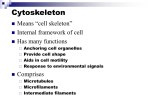
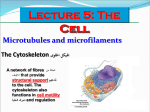
Cytoskeleton 5/29/12 Cytoskeleton • • • • Means “cell skeleton” Internal framework of cell Has many functions – – – – Anchoring cell organelles Provide cell shape Aids in cell motility Response to environmental signals Comprises – – – Microtubules Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Microtubules • • • Hollow tubes made of the protein tubulin – Alternating dimers of and tubulin Largest of cytoskeleton filaments Is used for: – – Maintenance of cell shape – Movement of organelles through cell • Often involves motor molecule – Often originate from centrosome Motility • Flagella or cilia Centrioles • • • • Located in centrosome of animal cells Occur in perpedicular pair Have 9 triplets of microtubules Facilitate microtubule assembly and chromosome separation in some cells Flagellum structure • Basal body links flagellum or cilia to cell surface – Basal body looks just like a centriole • • 9 +2 arrangement of microtubules Radial spokes prevent dramatic sliding and only bending Motor molecules • • Interact with tubulin or actin • Undulation-used for flagella and cilia movement – Two microtubules moving relative to one another • Organelle movement is like a ski lift tram or a monorail • • • Cell movement facilitated by flagella or cilia Are fixed at one end and allowed to move freely at the other end – Movement is directional Cell motility Unlike in prokaryotes, eukaryotic flagella undulate Cilia are small appendages and they move like a swimmers arm-active stroke and return stroke How cell movement works • • Dynein is motor molecule that interacts with tubulin Dynein walks along one microtubule, while bound to another – This results in bending – If no radial spokes or organelle coat, then microtubules would walk out of cell Microfilaments • • • • • • Made of two intertwined strands of actin Helps maintain cell shape – – Actin rearrangements allow engulfment events Psuedopod formation in ameoba Promote cytoplasmic streaming in plants Essential for muscle contraction Used by invading bacteria to move around cell Frequently being assembled and disassembled within cell Microfilaments 2 • • Myosin interacts with actin to cause contraction Cytoplasmic streaming and ameoboid motion are similar – Cortical cytoplasm around the perimiter of cell contains perpendicular actin (wind fence) – Streaming portion has parallel actin which facilitates cytoplasm movement – Plant cell wall prevents amoeboid movement of plant cell Intermediate Filaments • • • • Resemble cable in structure Are made of protein subunits Help maintain cell shape and keep organelles in place Are durable and not assembled and disassembled as other cytoskeleton components