* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 48 Worksheet
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
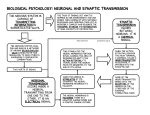
Vocabulary Box. -Glia Cells -Oligodendrocytes Distinguish between the central and peripheral nervous systems. -Schwann -Resting Potential -Ligand-Gated Channel -Voltage-Gated Channel Distinguish between the sensory and motor neurons. -Stretch-Gated Channel -neurotransmitters Chapter 48 Worksheet Label the following parts of a neuron. Signal Transduction. 1. Resting Potential: 2. Stimulus: 3. Depolarization: influx of Na+ in. 4. Repolarization Outline the main steps taking place in this picture: What part of the nerve are we looking at? What is an example of a neurotransmitter? 1. The part of a neuron that carries nerve impulses toward the cell body is called _____. a. a nerve b. white matter c. a neurotransmitter d. a dendrite e. an axon 2. Which one of the following statements is not true about the resting potential? a. The neuron's plasma membrane is much more permeable to potassium than to sodium. b. The concentration of sodium is much higher inside the cell than outside. c. The sodium-potassium pump plays a role in maintaining the resting potential. d. Inside the cell, the concentration of potassium is much higher than the concentration of sodium. e. All of these are true statements. 3. Which one of the following statements about the transmission across a typical chemical synapse is not true? a. Neurotransmitter molecules are stored in vesicles in the synaptic terminal. b. Action potentials trigger chemical changes that make the neurotransmitter vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane of the transmitting cell. c. Vesicles containing neurotransmitter molecules diffuse to the receiving cell's plasma membrane. d. Neurotransmitter molecules bind to receptors in the receiving cell's plasma membrane. e. The binding of neurotransmitter molecules to receptors transmits an impulse across a synapse. 4. A drug that causes potassium to leak out of a neuron, increasing the positive charge on the outside, would _____. a. make it easier to trigger action potentials in the neuron b. cause the cell to release its neurotransmitter c. speed up nerve signals traveling the length of the cell d. act as a stimulant e. inhibit transmission of nerve signals by the neuron 4. A physician friend of yours tells you about a patient with a head injury who suddenly stopped breathing during the examination. What portion of the brain was probably injured? a. medulla oblongata b. cerebrum c. cerebellum d. hypothalamus e. pituitary