* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
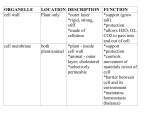
Cell Structure Characteristics and Functions Plasma (cell) Membrane (this refers to the membrane that surrounds the cell) Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear Envelope Stores DNA of a cell. (In a non-dividing cell, the DNA is in the form of chromatin) Contains Nucleolus Surrounded by nuclear envelope Site for ribosome subunit production It is found within the nucleus Ribosomes (free & bound) Vesicles Smooth ER Rough ER Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Vacuoles Regulates material entering and leaving the cell (selectively permeable) Made of phospholipids A double-membrane (2 phospholipid bilayers) that surrounds the nucleus Regulates material entering and leaving the nucleus (selectively permeable) Contains nuclear pores to allow things in and out the nucleus. Sole function is to make proteins. They are made of proteins and rRNA Consists of 2 subunits (large and small) Free ribosomes are suspended in the cytosol/cytoplasm and predominantly make polypeptides (proteins) needed by the cell. Bound ribosomes are attached to Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) predominantly make polypeptides (protein) to be exported (secreted) from the cell Membrane sacs that transport material throughout the cell. Labyrinth of membrane-bound tubes and sacs Synthesize lipids Breakdown carbs Detoxification (liver cells have extensive smooth ER) Labyrinth of membrane-bound tubes and sacs Contains ribosomes that primarily make polypeptides (proteins) for export / secretion Looks like a stack of pancakes It packages, stores, and ships material (proteins) from the ER to the cell membrane to be exported from the cell Membrane-bound sacs that contain hydrolytic enzymes used to digest/breakdown material The enzymes must be “locked” in the sac so that they don’t degrade the cell. Digest biological things for the cell (food, old organelles, bacteria) White blood cells have a lot Some non-plant cells have food vacuoles to store/hold food/nutrients. Plant cells have a central vacuole which is primarily used to store water. Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacteria Yes yes yes Yes Yes NO Yes yes NO Yes yes NO Yes yes YES Free In cytoplasm only! no ER Yes yes Yes Yes NO Yes Yes NO Yes Yes NO Yes Yes (this is debatable) NO Yes NO Yes (some) No Mitochondria Chloroplasts Peroxisomes Cytoskeleton Microfilaments Microtubules Intermediate filaments Centriole/centrosome (2 centrioles make up centrosome) Cilia/Flagella Cell Wall Many unicellular cells have a contractile vacuole to regulate internal water. In plants helps with turgor pressure Organelle where cellular respiration occurs. Oxygen is used to make ATP from macromolecules (glucose) Has a double membrane (2 phospholipid bilayers) The inner membrane has many folds (cristae) to increase surface area for respiration. Has its own DNA Get from your mother Organelle where photosynthesis occurs. Also has a double membrane. Contains stacks of thylakoids (grana) Thylakoids hold the pigments site of light reactions Stroma surrounds the thylakoids and is the site of the Calvin Cycle. Calvin Cycle makes sugar (fueled by ATP and NADPH from light reactions) Has its own DNA Membrane sacs with enzymes that breakdown toxic substances. (chemicals, pesticides, etc) The reactions make peroxide H2O2 Catalase is then used to breakdown the peroxide Provide shape and support for cells Microtubules also serve as “tracks” for structures to move across the cell Spindle fibers move chromosomes during Mitosis, Meiosis Barrel shaped structure made up of microtubules Used during cell division to produce mitotic spindle (spindle fibers) Cilia are hair-like structures Flagella are whip-like structures Cilia found in our respiratory tract Flagella found in sperm Unicellular organisms use for movement Provides shape, support, and protection for plant cells, bacterial cells Primarily made of cellulose (in plant cells) Yes Yes NO No yes NO Yes yes NO Yes yes NO Yes No No Yes (some) Yes (some sperm cells) No Yes Yes