* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOSKELETON NUCLEUS
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
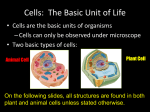
1/11/2017 CELL WALL • In Plants (not animals) • Outermost layer • Made of cellulose (type of sugar) and gives the cell strength CELL MEMBRANE CYTOSKELETON • Inside cell wall (for plants) • Outermost layer (for animals) • Two layer phospholipid • Phospho (end that contains phosphorous) hydrophilic: water –loving • Lipid hydrophobic: water fearing • Selectively permeable: • Controls what goes in and out of the cell • Inside cytoplasm NUCLEUS ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM • In cytoplasm • Holds DNA • Cookbook with recipes for making proteins • Proteins control chemical reactions • Sends out one recipe at a time • Acts as skeleton • Keeps cell membrane from collapsing • Acts as muscles • Helps some cells move • In cytoplasm: connected to the nucleus • The “factory” of the cell • Makes proteins, lipids and other materials • Rough ER (with ribosomes) or Smooth ER (no ribosomes) • When new cells are made, all of the DNA in a cell must be copied 1 1/11/2017 RIBOSOMES MITOCHONDRIA • In cytoplasm • In cytoplasm • Reads “recipe” of DNA • The “power plant” of the cell • Puts together amino acids to make proteins • Converts energy from Sugar into ATP • NOT covered by a membrane • Also in prokaryotes • Not an organelle • ATP is how cells store energy CHLOROPLASTS GOLGI COMPLEX • In cytoplasm of plants • In cytoplasm • The “UPS distribution center” of the cell • Packages and distributes proteins • Site of photosynthesis • Is green because of chlorophyll (pigment that traps light energy) • Makes glucose (result of photosynthesis) VESICLE • In cytoplasm • The “UPS truck” of the cell • Formed when a membrane surrounds material • Vesicles can move material into a cell, out of a cell and throughout the cell LYSOSOMES VACUOLE • In cytoplasm • In cytoplasm (more common in plants) • Special type of vesicle that contain enzymes • Plants: • Large central vacuole stores water • Can wilt when it loses water • May act like lysosome (digestion) • Digest and destroy waste and foreign invaders 2