* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells: The Basic Unit of Life
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
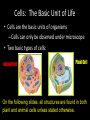
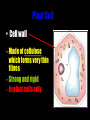
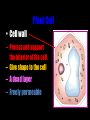
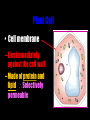
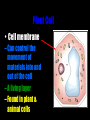
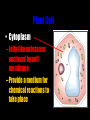
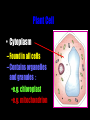
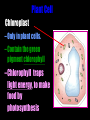
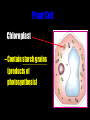
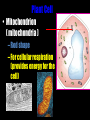
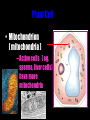
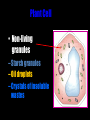
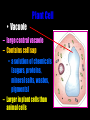
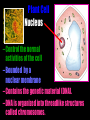
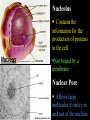
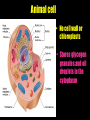
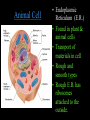
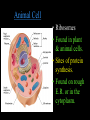
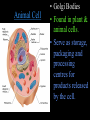
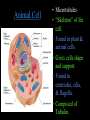
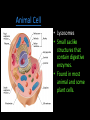
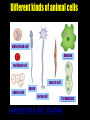
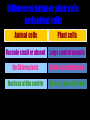
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life • Cells are the basic units of organisms – Cells can only be observed under microscope • Two basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell On the following slides, all structures are found in both plant and animal cells unless stated otherwise. Cell Biology Animations Plant Cell • Cell wall –Made of cellulose which forms very thin fibres –Strong and rigid –In plant cells only Plant Cell • Cell wall – Protect and support the interior of the cell. – Give shape to the cell – A dead layer – Freely permeable Plant Cell • Cell membrane – Lies immediately against the cell wall – Made of protein and lipid Selectively permeable Plant Cell • Cell membrane – Can control the movement of materials into and out of the cell – A living layer – Found in plant & animal cells Plant Cell • Cytoplasm – Jelly-like substance enclosed by cell membrane – Provide a medium for chemical reactions to take place Plant Cell • Cytoplasm – Found in all cells – Contains organelles and granules : •e.g. chloroplast •e.g. mitochondrion Organelles • very small size – some can only be observed under electron microscope • All organelles have specific functions • Found in the cytoplasm Plant Cell • Chloroplast – Only in plant cells. – Contain the green pigment chlorophyll –Chlorophyll traps light energy, to make food by photosynthesis Plant Cell • Chloroplast – Contain starch grains (products of photosynthesis) Plant Cell • Mitochondrion ( mitochondria ) – Rod shape – For cellular respiration (provides energy for the cell) Plant Cell • Mitochondrion ( mitochondria ) – Active cells ( eg. sperms, liver cells) have more mitochondria Plant Cell • Non-living granules – Starch granules – Oil droplets – Crystals of insoluble wastes Plant Cell • Vacuole – large central vacuole – Contains cell sap • a solution of chemicals (sugars, proteins, mineral salts, wastes, pigments) – Larger in plant cells than animal cells Plant Cell Nucleus – Control the normal activities of the cell – Bounded by a nuclear membrane – Contains the genetic material (DNA). – DNA is organized into threadlike structures called chromosomes. Nucleolus Contains the information for the production of proteins in the cell. Not bound by a membrane Nuclear Pore Allows large molecules to move in and out of the nucleus Different kinds of plant cells Onion Epidermal Cells Guard Cells root hair Root Hair Cell Cellular World - YouTube Animal cell • No cell wall or chloroplasts • Stores glycogen granules and oil droplets in the cytoplasm Animal Cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum (E.R.) • Found in plant & animal cells • Transport of materials in cell • Rough and smooth types • Rough E.R. has ribosomes attached to the outside. Endoplasmic Reticulum mitochondrion Animal Cell • Ribosomes • Found in plant & animal cells. • Sites of protein synthesis. • Found on rough E.R. or in the cytoplasm. Animal Cell • Golgi Bodies • Found in plant & animal cells. • Serve as storage, packaging and processing centres for products released by the cell. Animal Cell • Microtubules • “Skeleton” of the cell. • Found in plant & animal cells. • Gives cells shape and support. • Found in centrioles, cilia, & flagella. • Composed of Tubulin. Animal Cell • Lysosomes • Small saclike structures that contain digestive enzymes. • Found in most animal and some plant cells. Rough E.R. Different kinds of animal cells white blood cell Amoeba red blood cell muscle cell cheek cells sperm nerve cell Paramecium Journey Into a Cell - YouTube Similarities between plant cells and animal cells Both have a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm. Both have a nucleus. Both contain mitochondria, golgi bodies, E.R. , ribosomes and microtubules. Differences between plant cells and animal cells Animal cells Plant cells Relatively smaller in size Relatively larger in size Irregular shape Regular shape No cell wall Cell wall present Differences between plant cells and animal cells Animal cells Plant cells Vacuole small or absent Large central vacuole No Chloroplasts Chloroplasts Present Nucleus at the centre Nucleus near cell wall