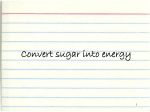* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7-2 EukCell Notes Wilson
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Notes 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Organelles : “________________________________________” inside a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into 2 major parts: the___________________ & the ___________________. Cytoplasm is the portion of the cell outside the nucleus cyto- = _____________ -plasm: _______________ _______________in cell The Nucleus: “_________________________” containing nearly all the cell's _________ (usually visible as granular material called___________________________) and the coded instructions for making __________________and other important molecules. Ribosomes: Ribosomes are small particles of _______and protein found throughout the ___________________ and on the________________________________________________. One of the most important jobs carried out in cell is_________________________– “____________________” Proteins are assembled on ribosomes. Endoplasmic Reticulum: ER (for short) _________________________of ER: _____________ and___________ depending on if they have ___________________or not “______________________” Golgi Apparatus appears as a ________________ of closely apposed membranes; modifies, sorts, and ____________________________and other materials from the ER for _______________in the cell or _____________outside the cell. “______________Center” Lysosomes : small organelles filled with ________________ that__________________, or breaks down, _______________, ___________________, and ______________ into small molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell. Also breaks down old useless organelles removing “junk” that might otherwise accumulate and clutter up the cell. “__________ ____” Vacuole: ______________________such as _______salts, proteins, & __________________. Central Vacuole: ___________________ vacuole filled with liquid in _______________cells helps in cell ________________. Vacuoles are also found in some __________________ organisms & in some ___________. The ______________________contains a _______________ ______________that pumps excess water out of the cell. Mitochondria: nearly all __________________ cells contain mitochondria - ______________ the chemical _______________stored in ___________ - (glucose) C6H12O6 into compounds (______) that are more convenient for the cell to use. The “_____________ Plant” of a cell. Chloroplasts In __________________and some other organisms. Capture energy from ___________________and convert it into chemical energy (glucose) C6H12O6 in___________________________. Contain the ______________pigment_________________. A little history about Mitochondria and the Chloroplasts – The _____________________________theory Chloroplasts and mitochondria contain their own ________________ other organelles ________________. Some scientists theorize they are the descendants of ancient prokaryotes that evolved a _________________ relationship inside early cells. Some had the ability to use oxygen to _________________________and evolved into mitochondria. Others carried out __________________________and evolved into chloroplasts. The cytoskeleton is a network of _____________________________that helps the cell to maintain its__________________ - also involved in__________________________________ -made up of: __________________________ and __________________________ Centrioles are located near the ___________________ and help to organize _______________________ In the nucleus of a cell, the DNA is usually visible as a dense region called the nucleolus. the nuclear envelope. granular material called chromatin. condensed bodies called chloroplasts. Two functions of vacuoles are storing materials and helping to break down organelles. assemble proteins. maintain homeostasis. make new organelles. Chloroplasts are found in the cells of plants only. plants and some other organisms. all eukaryotes. most prokaryotes. Which of the following is NOT a function of the Golgi apparatus? synthesize proteins. modify proteins. sort proteins. package proteins. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? manufactures new cell organelles assists in movement of some cells from one place to another releases energy in cells modifies, sorts, and packages proteins Notes 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Organelles : structures inside a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Cytoplasm is the portion of the cell outside the nucleus. cyto- = cell -plasm = fluid material in cell The Nucleus: cells control center containing nearly all the cell's DNA (usually visible as granular material called chromatin) and the coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules. Ribosomes: Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm. One of the most important jobs carried out in the cell is making proteins. Proteins are assembled on ribosomes. “Protein Factories” Endoplasmic Reticulum – ER (for short) two types of ER—rough and smooth depending on if they have ribosomes or not “Canal System” Golgi Apparatus appears as a stack of closely apposed membranes. modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic reticulum for storage in the cell or secretion outside the cell. “packaging Center” Lysosomes : small organelles filled with enzymes that digests, or breaks down, lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into small molecules that can be used by the rest of the cell. Also breaks down old useless organelles removing “junk” that might otherwise accumulate and clutter up the cell. “Suicide Sac” Vacuole: store materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. Central Vacuole: single vacuole filled with liquid which aids in cell support in many plant cells. Vacuoles are also found in some unicellular organisms and in some animals. Mitochondria: nearly all eukaryotic cells contain mitochondria. Mitochondria convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds more convenient for the cell to use. Chloroplasts In plants and some other organisms. Capture energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy (glucose) C6H12O6 in photosynthesis. The paramecium (single celled protest) contains a contractile vacuole that pumps excess water out of the cell. A little history about Mitochondria and the Chloroplasts – The endosymbiotic theory Chloroplasts and mitochondria contain their own DNA molecules – other organelles don’t. Some scientists theorize they are the descendants of ancient prokaryotes that evolved a symbiotic relationship inside early cells. Some had the ability to use oxygen to generate ATP and evolved into mitochondria. Others carried out photosynthesis and evolved into chloroplasts. This idea is called the endosymbiotic theory. The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that helps the cell to maintain its shape. The cytoskeleton is also involved in movement. The cytoskeleton is made up of: microfilaments microtubules Centrioles are located near the nucleus and help to organize cell division. In the nucleus of a cell, the DNA is usually visible as a dense region called the nucleolus. the nuclear envelope. granular material called chromatin. condensed bodies called chloroplasts. Two functions of vacuoles are storing materials and helping to break down organelles. assemble proteins. maintain homeostasis. make new organelles. Chloroplasts are found in the cells of plants only. plants and some other organisms. all eukaryotes. most prokaryotes. Which of the following is NOT a function of the Golgi apparatus? synthesize proteins. modify proteins. sort proteins. package proteins. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? manufactures new cell organelles assists in movement of some cells from one place to another releases energy in cells modifies, sorts, and packages proteins