* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell-Transport-Web
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
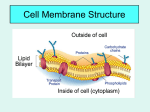
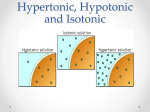
Name: _______________________________ Block: _______ Date: __________________ Cellular Transport Web Activity Activity 1: Types of Transport Log on to: http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/tdc02_int_membraneweb/ Click on “Instructions” and read the paragraphs. In order to maintain a stable environment or homeostasis, a cell must take in and let out certain substances. 1. What does a cell need to take in to survive? ______________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What does a cell let out? _____________________________________________________________ 3. Think: Provide an example of a substance that a cell would produce that other cells in the body would need. _______________________________________ Click on “Interstitial Fluid” and read the paragraphs. 4. Circle the correct answer: Interstitial fluid could also be called extracellular fluid / intracellular fluid. 5. Circle the correct answer: Cytoplasm could also be called extracellular fluid / intracellular fluid. Click on “Lipid Bilayer” and read the paragraphs. 6. The lipid bilayer is the major component of the plasma or cell membrane. What two characteristics of a molecule would NOT let it pass through the lipid bilayer easily? _________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click on “Plasma Membrane” and read the paragraphs. 7. Describe the three ways substances can enter or exit the cell. ________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click on “Protein Pump” and read the paragraphs. 8. What kind of cell transport does a protein pump perform? ___________________________________ 9. What does a protein pump require in order to move substances? _____________________________ Click on “GluT Transporter” and read the paragraphs. 10. Describe how the process of facilitated diffusion works. ____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ To fill out the table below, click on the different types of molecules, watch the animations, and read the paragraphs. Answer the additional questions that follow. Molecule Direction of Molecule Movement (High to Low Concentration or Low to High Concentration) Energy Required for Movement (Yes or No) Part of Cell Through Which Molecule Passes (Lipid Bilayer, Membrane Protein, or Vesicles) Type of Transport Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Diffusion Glucose Sodium Membrane Protein Low High Water Enzyme Yes 11. What is the relationship between oxygen, carbon dioxide, and glucose? _______________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What is exocytosis? Besides enzymes, what other substance is transported through exocytosis? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Activity 2: Osmosis in Cells Log on to: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/biocoach/biomembrane1/osmosis.html Osmosis (movement of water across membranes) depends on the relative concentration of solute molecules on either side of the membrane. The presence or absence of cell walls influences how cells respond to osmotic fluctuations in their environment. Click on Review Looking at the diagram above, describe the difference between the three types of solutions. The small circles represents dissolved solutes like salt, glucose, and amino acids. You can assume that the additional space surrounding the solutes is water. hypotonic - __________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ isotonic - ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ hypertonic - _________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click on Next Cells in Isotonic Solution 1. What is the concentration of salt in animal cells? _________________________ 2. When cells are in isotonic solution, is there movement of water into or out of the cell? If so, describe this movement. ______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click on Next Cells in Hypotonic Solutions Describe the net movement of water molecules when cells are placed in a hypotonic solution. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click on A Closer Look A Closer Look at Plant and Animal Cells in Hypotonic Environments **Make sure to ANIMATE the graphics.** 1. What happens to an animal cell when placed in a hypotonic solution? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Account for the different reactions between plant and animal cells when placed in a hypotonic environment. ________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click Back to Review then Next Cells in Hypertonic Solutions Describe the net movement of water molecules when cells are placed in a hypertonic solution. ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Click on A Closer Look A Closer Look at Plant and Animal Cells in Hypertonic Environments **Make sure to ANIMATE the graphics.** What happens to animal cells when placed in a hypertonic solution? ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ Activity 3: Movement Across a Membrane Go to: http://biologyonline.us/Online%20A&P/AP%201/Northland/AP1lab/Lab%20Online/Virtual%20Labs/ Transport%20Index.htm Directions: Read through the website and conduct the activities by following the instructions. Write 5 sentences explaining what each of the 3 experiments were demonstrating Experiment 1: Experiment 2: Expermiment 3: