* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ashley Ajayi
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Microtubule wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
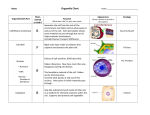
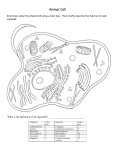
Ashley Ajayi Pd 4 Biology Paper: Cells (I will hand in diagram) Endoplasmic Reticulum is a network of membranous sacs and tubes. It is active in membrane synthesis and other synthetic and metabolic processes. It has two types; rough ER and smooth ER. Rough ER can be distinguished by its outer surface studded with ribosomes. While smooth ER lack ribosomes and therefore appears smooth under an electron microscope. The Nuclear Envelope is a double membrane enclosing the nucleus which helps to separate its contents from the cytoplasm. It is perforates by pores and in continuous with the Endoplasmic Reticulum. A Nucleolus is a nonmembranous organelle, located in the nucleus, involved in the synthesis of ribosomal DNA and production of ribosomes. A nucleus has one or more nucleoli depending n the species and the stage in the cell’s reproductive cycle. Chromatin is material consisting of DNA and proteins. It is visible as individual chromosomes in a dividing cell. The Plasma membrane encloses the cell. Ribosomes are nonmembranous organelles that consist of ribosomal DNA and protein that carry out the synthesis of proteins. They are free in cytoplasm, called free ribosomes or bound to rough ER or the nuclear envelope, called bound ribosomes. A Golgi Apparatus is an organelle that is active in synthesis, modification, sorting, and secretion of cell products. Here, products of the ER are modified and stored and then sent to other destinations. A Lysosome is a digestive organelle made up of hydrolytic enzymes that an animal cell uses to digest macromolecules and recycle intercellular materials a process called autophagy. The Mitochondrion is an organelle where cellular respiration occurs and most of a cell’s ATP is generated. It extracts energy from sugars, fats, and other fuels with the help of oxygen. It has at least two membranes that separate the innermost space from the cytosol. Ti has the ability to grow and reproduce with cell. Peroxisome is an organelle with various specialized metabolic functions. It produces hydrogen peroxide. Microvilli are projections that increase the cell’s surface area. The Cytoskeleton reinforces the cells’ shape and plays a major role in organizing the structures and activities of cells. It functions in cell movement. It is composed of three molecular structures made up of protein: microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. Microtubules help to shape and support the cell. They also serve as tracks along which organelles equipped with motor proteins can move. A Centrosome is a region where the cell’s microtubules are initiated. An animal cell contains a pair of centrioles composed of nine sets of triplet microtubules arranged in a ring. Flagellum is a locomotion organelle present in some animal cells. It is composed of membrane enclosed microtubules.