* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.2 Notes
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
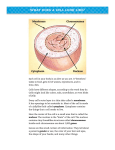
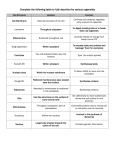
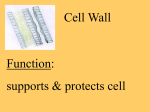
1.2 Notes Cell Part Type of Cell Location Shape Function Cell Wall Plant, Bacteria, and some others Outermost layer Typically rectangular Structure and support Cell Membrane All Surrounding cell Any Nucleus All except bacteria Inside cell Round Nuclear Membrane All except bacteria Surrounding nucleus Round Chromatin All except bacteria Inside nucleus Strands Nucleolus All except bacteria Inside nucleus Round Protects cell by controlling what goes in and out of cell Directs cell’s activities Protects nucleus by controlling what goes in and out of nucleus Contains genetic material Makes ribosomes 1.2 Notes Mitochondria (singular: mitochondrion) All Cytoplasm Kidney bean shape Produce energy Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) All Cytoplasm, near nucleus Squiggly Passageway for proteins and other materials Ribosomes All On ER and in cytoplasm Small dots Produce proteins Chloroplasts Plant and some others Cytoplasm Green ovals Lysosomes Animal and some others Cytoplasm Round Capture sunlight to produce food through photosynthesis Break down food and old cell parts Vacuoles All Cytoplasm Large or small, rounded Storage for food, water, and waste products Golgi Bodies All Cytoplasm Flat tubes Receive, package, and deliver proteins and other materials