* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
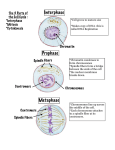
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Chapter 5 Belk and Borden Biology: Science for Life Cell Division • - the process a cell undergoes in order to make copies of itself. • Why do cells divide? What is Cancer? • “mitosis gone mad” • - a disease that begins when a single cell escapes from the regulation of its own division • Tumor • Benign vs Malignant The Cell Cycle • -all the events that occur when a cell divides • -time required can vary from minutes to days, depending on the cell – Salmonella = 29 min – Red B. C. = 120 days DNA & Chromosomes • DNA as chromatin strands and chromosomes • Sister Chromatids • Centromere • Why do chromosomes form? Interphase (G1, S, G2) (about 90% of the cell cycle time) • Cell grows during all 3 subphases by making proteins and organelles • G1 = first growth phase Interphase (G1, S, G2) (about 90% of the cell cycle time) • S phase = DNA is copied (synthesis) so each daughter cell has a complete set of chromosomes at the end of the cell cycle Interphase (G1, S, G2) (about 90% of the cell cycle time) • G2 phase = second growth phase • All through interphase, the cell is fulfilling its function • At maximum volume to surface ratio, cell either remains in interphase or enters mitosis Mitosis: Prophase • Chromatin condenses into chromosomes • Each duplicated chromosome appears as 2 identical sister chromatids • Mitotic spindle begins to form in cytoplasm Mitosis: Prometaphase • Nuclear membrane disintegrates • Spindle fibers interact with chromosomes • The “dance of the chromosomes” begins Mitosis: Metaphase • Chromosomes are aligned at middle of cell • Identical chromatids of each chromosome are attached to spindle fibers radiating from opposite poles of the cell Mitosis: Anaphase • Paired centromeres of each chromosome separate, freeing sister chromatids from eachother • Each chromatid now a chromosome • Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell Mitosis: Telophase • 2 new nuclei form at two poles of the cell where chromosomes have gathered • Chromosomes uncoil and revert to chromatin form • Mitosis (division of one nucleus into two identical nuclei) is complete Cytokinesis Allium root tip (onion) a mitosis classic! Classify Cells relative to Cell Cycle Phase link Control of the Cell Cycle • Cells require nutrients and growth factors to divide (example PDGF & fibroblasts) • Density dependent inhibition also regulates cell division • Adhesion of cells is also involved. Cells normally stop dividing if they lose their anchorage. • The role of regulatory proteins at the G1 “restriction point” is also critical. Control of the Cell Cycle • Regulatory proteins pace and control cell cycle events at “checkpoints” • G1 checkpoint—monitors nutritional status, growth factors, & cell density; “restriction point” • G2 checkpoint—monitors DNA replication and cell size • Metaphase checkpoint—monitors chromosome attachment to spindle fibers Mutations • Changes (errors) in the genes that code for cell cycle regulatory proteins and tumor suppressor proteins are involved in cancer • Proto-oncogenes code for growth factors • Mutated proto-oncogenes (oncogenes) can overstimulate cell division and override the G1 checkpoint • Mutated tumor supressor genes fail to produce the proteins that prevent tumors Healthful Decisions to reduce Cancer Risk • • • • • • Avoid carcinogenic addictions! Eat whole foods (fresh fruit and grains) Exercise regularly to boost immune system Don’t drink alcohol in excess Don’t get sunburned Undergo regular screening and selfexamination