* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Cycle and Cancer
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
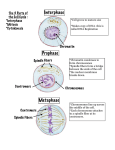
The Cell Cycle and Cancer Study Guide 1. What is the cell cycle? The regular sequence of growth and division cells undergo. 2. What are the three stages of cell division? Interphase – Mitosis - Cytokinesis 3. What is mitosis? The stage of cell division in which the nucleus divides into two nuclei; in this stage one copy of the DNA is copied (replicated) and distributed to each new daughter cell. 4. List the four phases of mitosis? Prophase – Metaphase – Anaphase - Telophase 5. In which stage does the cell spend most of its time? Interphase 6. What happens in prophase? The chromatin condenses (thickens) to form chromosomes; spindle fibers form; the nuclear membrane breaks down; 7. What happens in metaphase? The chromosomes line up in the center of the cell; each chromosome attaches to the spindle fiber at the centromere; 8. What happens in anaphase? The centromere splits and the two chromatids separate to opposite ends; 9. What happens in telophase? The chromosomes stretch and lose their rod like appearance; a nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes; 10. What is cytokinesis? The cell membrane pinches in around the middle of the cell; each daughter cell ends up with the same number of identical chromosomes as the parent cell; 11. What is replication? Replication is when the cell makes a copy of the DNA in its nucleus during interphase; 12. What are centrioles? These are barrel-shaped structures that take part in creating the spindle fibers during cell division. 13. What is chromatin? Thread-like strands of DNA before replication takes place during interphase. 14. What are chromatids? One of the identical rods of a chromosome. 15. What is centromere? The button-shaped structure that holds the sister chromatids together. 16. What are chromosomes? A double rod of condensed chromatin. 17. Draw and label the parts of a chromosome. See page 63 18. What is DNA? The genetic material in the nucleus of the cell. 19. What is the name of the structure given to DNA? double helix 20. What molecules make up the sidebars of the DNA molecule? Deoxyribose (sugar) – phosphate molecule 21. What molecules make up the rungs of the DNA molecule? Nitrogen bases 22. Name the nitrogen bases in DNA and describe how they pair up. adenine-thymine cytosine-guanine 23. What is cancer? A disease in which cells grow and divide uncontrollably. 24. How does a tumor form? A tumor is a mass of abnormal cells that develops when cells divide and grow uncontrollably. 25. Name three ways that cancer can be treated. surgery – radiation - chemotherapy 26. What is chemotherapy? The use of drugs to kill cancer cells. 27. What is radiation treatment? Use of high energy waves to shrink the size of a tumor. 28. Name two health habits that can help prevent cancer. No smoking - eating a low fat diet – wearing sunscreen when out in the sun 29. What causes most cancers? smoking 30. What is the leading cause of lung cancer? smoking