* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jeopardy—Biology The Cell Rules: - answers do not have to be in
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
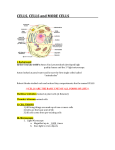
Jeopardy—Biology The Cell Rules: - answers do not have to be in question form - each correct answer is worth one point - each incorrect answer takes a point away - if an answer is given out of turn, that team loses a point and all other groups are given a point 1. Does a cell becomes more efficient or less efficient at life processes as it gets larger? less efficient 2. Name the type of cell that has no membrane-bound nucleus and no organelles. prokaryote 3. What are the two main components that make up the cell membrane? phospholipids and proteins 4. What is the name for the 2 layers of phospholipids in the cell membrane? lipid bilayer 5. The polar head groups of phospholipids face towards the outside of the cell and the inside of the cell because they are___________________? hydrophilic (water-loving) 6. The fatty acid tails of phospholipids orient themselves towards the inside of the cell membrane because they are__________________? hydrophobic (water-fearing) 7. Name a function of the golgi apparatus. process (or modify) proteins, package proteins for transport outside cell 8. Name two organelles present in plant cells but not in animal cells. cell wall, chloroplasts, large central vacuole 9. The cell membrane lets some things into cell and not other things. This property means that the cell membrane is_______________________. selectively permeable 10. Name two substances that are able to get through the lipids of the cell membrane. CO2 and O2 11. Name a type of protein found in the cell membrane. marker protein, receptor protein, channel (or transport) protein 12. Name two substances that can’t get directly through the lipids and have to use a channel protein. water, ions, any charged substance 13. Muscle cells need lots of energy, so they have lots of this organelle. mitochondria 14. In a eukaryotic cell, DNA is found in the _________________. nucleus 15. Who was the first person to see dead cells (cork) under a microscope? Robert Hooke 16. List the 3 parts of the cell theory. - all living things are made of cells - the cell is the most basic unit of life - cells only come from other cells 17. Draw the structure of the lipid bilayer. 18. Who was the first person to see living cells under the microscope and is known as the Father of the Microscope? Anton Van Leeuwenhoek 19. Name a cell that is not microscopic. chicken egg, human egg, some nerve cells(neurons) 20. Does a cell’s structure (what it looks like) have anything to do with its function (what it does)? yes, what a cell looks like (shape, size, etc) is related to what it does. 21. What is the average size of a bacterial cell in microns? 1 micron 22. Which is larger in general, an animal cell or a plant cell? plant cell (30 to 50 microns). Animal cells are smaller at 10 to 30 microns. 23. As a cell gets larger, the surface area to volume ratio decreases, meaning that the ____________ increases at a slower rate than the ______________. surface area, volume 24. Name the cell that has a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. eukaryote 25. Explain how an organelle of a cell is like an organ in your body? Just like every organ does a specific job to keep the body alive, every organelle does a specific job to keep the cell alive. 26. The model that represents how proteins, phospholipids, and other cell membrane components are able to move around within the cell membrane is called the___________________________. Fluid Mosaic Model 27. Draw a picture of the cell membrane showing where a peripheral protein might be located. peripheral protein would be found on the inner or the outer surface of cell memb. 28. What does a channel (or transport) protein in the cell membrane do? transports water, ions, or anything charged that can’t get through the lipid bilayer on its own 29. What is the role of a receptor protein on the cell membrane? receives outside information and transmits it into the cell 30. The organelle that uses sunlight to make food for the plant during photosynthesis. chloroplast 31. The region of the cell between cell membrane and nucleus where the organelles are found. cytoplasm 32. The gelatin-like fluid in the cytoplasm that bathes the organelles. cytosol 33. Cilia and flagella are used to help with movement. How are cilia and flagella different from each other. cilia: short, many flagella: long, few 34. Name two organelles that are part of the cytoskeleton and tell what they are made of. microtubules, microfilaments made of protein 35. What is the function of the golgi apparatus? processes, modifies, packages proteins 36. Draw a quick picture of a cell showing the nucleus and the nucleolus. Where are ribosomes made? nucleolus 37. What is the dump or recycling center of the cell? And why is it called the dump or recycling center? lysosome. Contains enzymes that break down molecules, old organelles and foreign substances. 38. What is the system of tubes and sacs that transports molecules such as proteins within the cell? Endoplasmic reticulum. 39. Draw a sketch of the rough ER and tell why it’s called rough. has ribosomes 40. Write down the pathway of protein starting from when they are first made until they leave the cell. ribosomes, rough ER, golgi, fuse with cell membrane 41. What is the name of the green algae that is studied by scientists because it appears to straddle the border between unicellular organisms and multicellular organisms? Volvox 42. Write down the steps in the theory on how multicellular organisms came to be. prokaryotesunicellular eukaryotescolonial organismsmulticellular organisms 43. Name the five stages of body organization in multicellular organisms from least complex to most complex. cellstissuesorgansorgan systemsorganism 44. What organelle provides support and protection in plants? cell wall 45. Write down the formula for calculating total magnification. eyepiece lens magnification x objective lens magnification 46. When viewed through a microscope, all objects are distorted. Describe exactly what happens to the object because of the lenses in the scope. object gets turned upside down and backwards. 47. What is the function of the diaphragm on a microscope? allows different amounts of light to pass through the specimen