* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System: Reflexes and Peripheral Nervous System
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
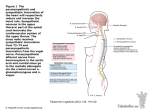
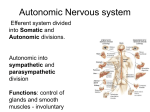
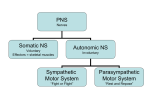
Chapter 7: Reflexes & Peripheral Nervous System Reflexes automatic responses to specific stimuli somatic − pull hand away from hot object autonomic − pupil dilation Reflexes occur over neural pathways called reflex arcs involve CNS? involve PNS? Reflexes two-neuron reflex arc − patellar or knee-jerk three-neuron reflex arc − flexor or withdrawal reflex − delay at synapse Reflexes Reflexes many only involve spinal cord some involve brain − pupil dilation − those integrating many different types of information testing evaluates condition of NS Peripheral Nervous System nerves and ganglia outside CNS nerve = bundle of neuron fibers outside CNS Structure of a Nerve wrapped in connective tissue like muscle endoneurium − perineurium − surrounds each fiber or process surrounds one fascicle epineurium − surrounds groups of fascicles Cranial Nerves primarily serve head and neck numbered in order Oh, oh, oh, to touch and feel very good velvet, ah. Spinal Nerves split into dorsal and ventral rami (ramus = branch) − dorsal: posterior sensory and motor − ventral intercostal nerves: anterior trunk sensory and motor cervical and lumbar nerves: form plexuses Nerve Plexuses network of nerves motor and sensory 4 plexuses − cervical − brachial − lumbar − sacral Nerve Plexuses Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) division of PNS motor controls involuntary − cardiac muscle − smooth muscle − glands contributes greatly to stable internal environment Somatic vs. Autonomic differ in: − effector organs − neurotransmitters − motor pathways somatic: one motor neuron autonomic: two motor neurons Somatic vs. Autonomic Somatic vs. Autonomic ANS two arms with opposing effects − sympathetic: mobilizes body during fear, rage, etc. − parasympathetic: calms down Parasympathetic Anatomy cranial nerves − sacral nerves − III, VII, IX, and X (vagus) pelvic splanchnic nerves terminal ganglion − synapse with 2nd motor neuron − close to organ Sympathetic Anatomy thoracolumbar division − ramus communicans - communicating branch sympathetic chain − thoracic & lumbar nerves lies along sides of vertebral column ganglia: cluster of cell bodies − − sympathetic chain collateral Sympathetic Pathways sympathetic chain ganglion − at same level − at different level – moves along chain − to skin collateral ganglion anterior to vertebral column − splanchnic − to viscera Sympathetic Pathways Autonomic Functions most organs receive fibers from both antagonistic effects Autonomic Functions postganglionic axons release different neurotransmitters − parasympathetic fibers are cholinergic − acetylcholine sympathetic fibers are adrenergic norepinephrine-precursor to epinephrine (adrenaline) Sympathetic Division fight or flight help cope with stressor − increase in heart rate − increase in bp − increase in blood glucose hormones destroyed by liver instant calm down? Parasympathetic resting and digesting decreases demands on cardiovascular system − bp and heart rate at normal − skin is warm − pupils constricted Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are in balance